* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
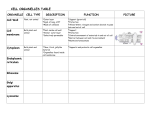
Name: Shane Peterson Textbook Title: diversity of living things Chapter Title: muti-cellular organisms Section Title: muti-cellular organisms met in different way Name: Shane Peterson Learning Targets *(underline KWST) Research on the learning targets Inside cells are organelle. These structures have a Life Science job or function to do. The function the structures do are critical for the cell to stay alive. 1I can describe relationships between structure and function at biological levels of organization. a. I can identify the biological levels of organization in order of least complex to most complex. b. I can describe how specific structures The organelles in a cell each have a function that (cellular organelles) enable the system to they need to do. If one organelle does not function function as a whole then the cell can’t survive. Keystone Biology 2BIO.A.1.2 - Describe relationships In cells are organelles, these organelles each have between structure and function at biological a job to do. If the job does get done the cell can die. levels of organization. b. BIO.A.1.2.2 - Describe and interpret relationships between structure and function at various levels of biological organization (i.e.,organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms). .Objectives: 1.Animal cell vs Plant cell Animal and plant cells have very similar organelles but, a plant cell has a cell wall and a vacuole and a animal cell doesn’t . 2.Cell Theory Every living thing is made up of cells, cells come from preexisting cells, and cells are the building blocks of life. 3.Cell organelles Every cell has an organelle to complete a ask to survive. Example: the nucleus process in formation. Name: Shane Peterson 4.Respiration vs Photosynthesis In photosynthesis cabin dioxide is turn into oxygen and sugar. While in respiration oxygen is turn into cabin dioxide 5.Simple Diffusion The materials diffuse across the cell membrane at a higher concentration to a lower concentration. 6.Specialization Unicellular organisms have many jobs to do in a single cell *KWST – Key Word Search Terms Name: Shane Peterson Headings, Subheadings and Questions Answers The microscope is an important tool. Why is the microscope an important tool? The invention of the light microscope led to the discovery of cells and to the development of cell theory. Cells are diverse. How are cells diverse? Scientists separate cells into two broad categories based on one key difference: the location of the genetic material cells need to reproduce and function. In a (yoo-KAR-ee-AHT-ihk) the genetic material is in a structure called the (NOO-klee-uhs), a structure enclosed by its own membrane. Scientists use the word (AWR-guh-NEHL) to describe any part of a cell that is enclosed by membrane. Plants and animals have eukaryotic cells. How are plants and animals different? Surrounding the nucleus is the cytoplasm. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cytoplasm and the outside of the cell. Plant cells also have cell walls. A is a tough outer covering that lies just outside the cell membrane. The cell wall supports and protects the cell. Having a cell wall is one important way in which plant cells differ from animal cells. Name: Shane Peterson Structures That Process Information What are the structures that process information? Organelles That Provide Energy What are the organelles provide energy? Organelles That Process and Transport What are some organelles that process and transport? Organelles for Storage, Recycling, and Waste What some of the organelles use for storage, recycling and waste? The nucleus is often the largest organelle in a cell. It contains all the information a cell needs to function. Within plant cells are (KLAWR-uh-PLASTS), organelles in which the energy from sunlight is used to make sugar. The endoplasmic reticulum is also part of the cellular transport system. Portions of endoplasmic reticulum break off to form small packages called vesicles. Inside cells are sacs called vacuoles. Vacuoles are made of membrane and can hold water, waste, and other materials. Vacuoles function with the cell membrane to move materials either into or out of the cell. Name: Shane Peterson Vocabulary: *If an affix or compound word, break the word into two parts and complete Part 1 and Part 2 by defining each part. *Use Google Translate to find the Latin, Greek, French, or Spanish. Try to find versions of the term that are similar to the English version. *Use your science textbook first, the science dictionary second, and dictionary.com last Term: cell membrane Affix - Compound - Simple Sentence: all cells have cell membrane Definition: a protective covering that covers the cell. Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Part 2: Latin or Greek: French or Spanish: Term: cytoplasm Affix - Compound - Simple Sentence: in side the cell membrane is the cytoplasm Definition: a gelatin-like fluid Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Part 2: Latin or Greek: French or Spanish: Term: eukaryotic cell Sentence: all eukaryotic cells have nucleus Definition: has a nucleus Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Latin or Greek: Affix - Compound - Simple Part 2: French or Spanish: Term: nucleus Sentence: a nucleus has genetic material Definition: a structure that has genetic material inside of it Affix - Compound - Simple Name: Shane Peterson Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Latin or Greek: Term: organelle Sentence: the mitochondria is an organelle Definition: any part of the that does a function Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Latin or Greek: Term: prokaryotic cell Sentence: prokaryotic cells have no nuceus Definition: a cell that has no nucleus Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Latin or Greek: Term: Sentence: Definition: Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Latin or Greek: Term: Sentence: Definition: Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 1: Latin or Greek: Term: Sentence: Definition: Similar or example: Opposite or non-example: Part 2: French or Spanish: Affix - Compound - Simple Part 2: French or Spanish: Affix - Compound - Simple Part 2: French or Spanish: Affix - Compound - Simple Part 2: French or Spanish: Affix - Compound - Simple Part 2: French or Spanish: Affix - Compound - Simple Name: Shane Peterson Part 1: Latin or Greek: Part 2: French or Spanish: