* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download review sheet
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
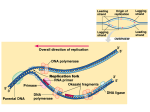
NAME:____________________________ MODERN GENETICS REVIEW QUESTIONS I - HONORS 1. Consider the following diagram of a DNA molecule: a. Label the diagram with the following terms: hydrogen bond, phosphodiester bond, deoxyribose, phosphate group. (Use each term only once) b. Label ALL the nitrogenous bases present with the appropriate letter (A,C,G,T). c. What part of the DNA molecule actually contains the hereditary information? 2. Briefly describe the process of replication. Where in the cell does replication occur? When in the cell cycle does replication occur? 3. List three ways in which RNA is different from DNA. (One of the listed differences must be the difference in nitrogen bases) 4. What does the “m” in mRNA stand for? Briefly describe its role in protein synthesis. 5. Why is the sequence of amino acids in a protein so important in the functioning of that protein? 6. Consider the following diagram pertaining to a part of protein synthesis: a. Label the diagram with the following terms: codon, anti-codon, peptide bond, ribosome, tRNA, mRNA, amino acid, polypeptide (Use each term only once) b. What is the name of the process pictured above? c. Where in the cell is this process occurring? d. Briefly describe tRNA’s role in the process pictured above. e. What ultimately determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein? 7. The following sequence of nucleotides was found on a segment of DNA: GGA CCT AAT CAC ATA GGG a. If the sequence located above was a gene on a chromosome and was used to create mRNA, what sequence would the resulting strand of mRNA have? b. If the mRNA was then translated into a protein, what would the sequence of amino acids be? 8. What is a mutation? 9. Briefly explain how a mutation could affect the shape and therefore function of protein molecule?