* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Study Guide to Chapter 5 – DNA In the end of chapter exercises: Important definitions to know : Gene DNA Genome Mutation Transcription Translation Genetic engineering Multiple choice questions 1-5, 7-9, 11,15,16. In the short answer questions, do all of them, 1-5. Added questions: 1. DNA is made of units called ______________. (A. amino acids, B. fatty acids, C. nucleotides). Each nucleotide has 3 parts. The _________ and __________ , and the _________. The genetic information resides in what part of the molecule? _______________________. What is the general shape officially called? ______________________. 2. Name the four nitrogenous bases in the molecule, and their letter abbreviations. A always pairs with _____ in DNA. G always pairs with _____ in DNA. 3. RNA is an intermediary in making a protein. The first step is called ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ____________ a) mRNA b) tRNA arrives at the ___________a) ribosome b) nucleus, where complementary _______________ a) mRNA b) tRNA build a polypeptide or protein which is a sequence of _____________ a) sugars b) phosphates c) amino acids. _________ bases (one, two, three) in the mRNA code for a single type of amino acid. After the protein is made it detaches from mRNA. 4. What is a mutation? Describe the following mutations: Point mutation: Substitutions Insertions and deletions Chromosomal aberrations 5. For what discovery did Watson and Crick win the Nobel Prize? 6. What is the Human Genome Project? What did it do?








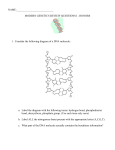



![trans trans review game[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013598402_1-2e1060ebd575957e2fb6f030e0a3f5e0-150x150.png)