* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
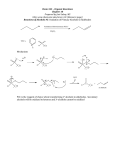
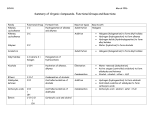
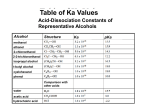
CHAPTER THIRTEEN: STRUCTURE AND SYNTHESIS OF ALCOHOLS 1. Structure/ Properties a. Nomenclature b. Relative Boiling points, solubility: hydrogen bonding c. Acid/Base behavior i. pKa of MeOH ≈ 16 ii. Acidity trends with branching near C-OH: branching hinders anion solvation iii. Basicity of neutral alcohol (pKb(A-) = 14.0 - pKa(HA)) iv. Basicity of alkoxide ion v. Formation of alkoxide ion by reaction of alcohols with Na° or K° 2. Preparation of Alcohols a. 1° alcohols from 1° Alkyl Halides with hydroxide (SN2, review) b. Vicinal Diols from anti-addition of water to Epoxides under acidic or basic conditions (review) or from oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 (review) c. Via Grignard RMgX or RLi i. Formation of Grignard or Alkyl Lithium from alkyl halides ii. reaction with Ketones and Aldehydes iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduction of Ketones, Aldehydes and Epoxides with either NaBH4 or LiAlH4 ii. Reduction of Esters and Carboxylic Acids with LiAlH4 only LEARNING OUTCOMES: Understand the formation of alcohols through use of organometallics in carboncarbon bond forming reactions with electrophiles Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Propose a reaction or sequence of reactions to produce a target alcohol in high yield. Predict the relative acidity of alcohols within a functional group class and compared to other functional groups. Predict the relative boiling points of alcohols within a functional group class and compared to other functional groups. Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and reactivity. SAMPLE EXAM PROBLEMS: 1. Draw the product of 3-(2-bromopropyl)-6,6-dimethylheptan-2-ol reacting with 2. Give the major organic product of the following reaction and include all stereoisomers formed: