* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cornell Notes Template - Paint Valley Local Schools
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
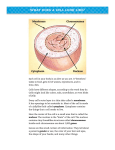
Cell Cornell Notes Cells Name ________________ # ____ Biology: The Science of Life: The Living Cell Video (United Streaming) =the simplest structures that can carry out all of the characteristics of life =Are they able to perform the characteristics necessary for life? Y or N Organisms can be: 1. multicellular 2. unicellular = = Where did the 1st cells come from? =all cells descended from the same unicellular organism that developed from nonliving materials over ______ billion years ago Example: Example: Cell Structures/Organelles Protoplasm (Cytoplasm) =a living, jelly-like substance; has a network of tiny tubules called _________________ which forms the cytoskeleton which supports the cell and gives it strength Cell (Plasma) Membrane =the “skin” that wraps around the cytoplasm; very important b/c it regulates what ___________ and ___________ the cell (semi-permeable) -into cell: 1. 2. 3. 4. -out of cell: 1. 2. 3. Cell Wall (plants, fungi, and monerans only) =functions to provide extra _____________ and ______________ Nucleus (found in all cells but monerans) Nuclear Membrane (nuclear envelope) = the _________ center of the cell - organisms that have a true nucleus are _________________ and those that do NOT have a true nucleus are called ____________________ = a double-layered membrane that covers the _______________; it is covered with _____________ that allow substances to enter and leave Chromatin =make chromosomes (DNA) when the cell is dividing (reproducing); has instructions for the cell’s activities; DNA is copied here enters cytoplasm thru n. pores Nucleolus =the denser area of the nucleus where ribosomes are made; literally means “little nucleus” Ribosomes =DNA from the nucleus travels to this structure with instructions for making a specific type of _____________; found in cytoplasm & RER -proteins can be used to build/repair cells, ___________ disease, transport substances across the cell ______________, or act as _____________________ (speeding up chemical reactions) Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 types (rough and smooth) Golgi body (Golgi apparatus) =a complex network of hollow passageways which extends into the cytoplasm RER= found close to the nucleus and is a place where ribosomes attach and proteins are made, packaged, and transported thru the cytoplasm SER- not usually found in abundance but is a place where proteins, lipids, and ions can be stored for later use; has no ribosomes =a collection of flattened, slightly curved sacs which ________ out proteins and wrap them in a membrane and _______ them where needed; found closer to the cell membrane of the cell How does a cell take in raw materials? Food vacuole =pinched in area of the cell membrane that forms when cell needs to take In food; cell eating is known as _________________ Lysosomes =a special structure made by the Golgi bodies functions to ____________ the food particle into nutrients which enters cytoplasm and can be used by the cell as an energy source =can also function to digest old, worn out ___________________ Mitochondria =energy is ________________ into these tiny, peanut-shaped organelles -called the ___________________________ of the cell -responsible for cellular respiration C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + ATP (energy for cells to do work) Plant & Animal Cell Differences Plants cells have: 1. a cell wall (already discussed) 2. a large central _________________ - which stores water with dissolved minerals and nutrients 3. _______________________ which contain chlorophyll; responsible for taking in sunlight and converting it into carbohydrates Equation for Photosynthesis CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2 Summary