* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Biology Test Review Sheet: Chapter 5 Plasma Membrane
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
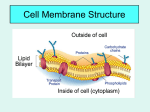
Honors Biology Test Review Sheet: Chapter 5 Plasma Membrane Structure and Types of Transport across the Plasma Membrane Tests will usually be given in a 55 minute period. During that time you will be asked to answer multiple choice, matching, and/or diagram analysis questions whose answers will be placed on a Scantron sheet. This is one of two parts to each test. The second part is a Short Answer part which requires you to write complete sentence answers to a variety of questions. The questions may be for you to explain, analyze or formulate an answer to an essay type question. For each test, you will be required to bring a pencil and a pen. All scan-tron is completed in pencil and the short answer can be done in either pen or pencil. Test topics that will be covered on the Chapter 5 Test will come from sections 1-9 and 28.3 (this is an example of active transport). You should be able to answer all these questions below. 1. Label a diagram of a plasma membrane. 2. Describe what the plasma membrane looks like. Review Fluid Mosaic Model. 3. Which part of the phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic? Hydrophilic? 4. Explain why the heads of the phospholipid molecule face towards the inside and the outside of the cell. 5. State the function of the plasma membrane. 6. What is the role of cholesterol in the plasma membrane? 7. What is the role of transport proteins in the plasma membrane? 8. Define diffusion. 9. Why can oxygen and carbon dioxide diffusion easily “through” the membrane? 10. What is meant by moving “with the concentration gradient” and “against the concentration gradient”? 11. Define osmosis. Is this an example of active or passive transport? 12. What is a solute molecule? 13. What determines the direction of water movement across the plasma membrane? 14. Define hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions. 15. Study Figure 5.5 on page 77. How does a plant cell respond to a hypotonic solution, isotonic solution? hypertonic solution? 16. What does turgid, flaccid and plasmolyzed mean as it relates to plant cells? 17. What prevents a plant cell from bursting when too much water enters it? 18. Why is it best for an animal cell to be in an isotonic environment? 19. Be able to predict in which direction water molecules will move. 20. Be able to state whether a solution is hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic. 21. Describe facilitated diffusion. 22. What is an aquaporin? What is it used for? 23. Define active transport. 24. Describe how the Sodium-Potassium Pump protein works to move sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. 25. Why does the sodium-potassium pump require ATP? 26. What happens to ATP when it transfers energy to be used for work? Think about the sodiumpotassium pump. 27. What is the reason your cells have the sodium-potassium pump? 28. Draw a diagram of a resting cell membrane. Be able to draw in all channel proteins, pump proteins. See notebook. 29. What makes the inside of the cell more negative than positive? 30. Define exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis and pinocytosis.