DNA Discovery - Biology Junction
... Part of the double helix is unwound Replication in small pieces (Okazaki fragments) Enzyme stitches pieces together later ...
... Part of the double helix is unwound Replication in small pieces (Okazaki fragments) Enzyme stitches pieces together later ...
Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid set of chromosomes in eukaryotes, in a single chromosome in bacteria, or in the DNA or RNA of viruses. i.e. an organisms genetic material. Chromosome: A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ...
... Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid set of chromosomes in eukaryotes, in a single chromosome in bacteria, or in the DNA or RNA of viruses. i.e. an organisms genetic material. Chromosome: A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
Name
... Review: DNA, Transcription, Translation Directions: Use this as a study guide for your next exam. Typically 80-90% of the exam questions come from this sheet. Other questions may come from labs, online activities and news articles which have been discussed in class. DNA and Chromosomes ...
... Review: DNA, Transcription, Translation Directions: Use this as a study guide for your next exam. Typically 80-90% of the exam questions come from this sheet. Other questions may come from labs, online activities and news articles which have been discussed in class. DNA and Chromosomes ...
DNA Workshop - Lapeer High School
... First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and go through the animation. You can repeat if necessary. a. What kind of protein unzips the DNA to start the process? b. Which bases always pair with each other? c. Where in the cell does replication take plac ...
... First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and go through the animation. You can repeat if necessary. a. What kind of protein unzips the DNA to start the process? b. Which bases always pair with each other? c. Where in the cell does replication take plac ...
GBE 214 TECNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... Course Title : TECNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Year : II Semester : IV Hours/Week : 5 ...
... Course Title : TECNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Year : II Semester : IV Hours/Week : 5 ...
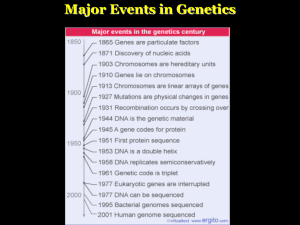
Major Events in Genetics
... – Produced a picture of the DNA molecule using this technique – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
... – Produced a picture of the DNA molecule using this technique – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
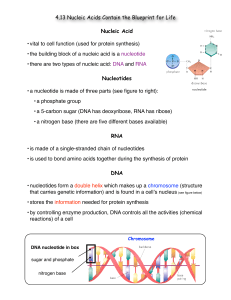
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
Study_Guide
... made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Describe, with th ...
... made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Describe, with th ...
7.1 - DNA Structure
... holding the DNA in place. This structure allows the long DNA molecules on the nucleus to be condensed into a much smaller space. Together, the histones form ‘beads’. However, there are also other proteins present in the chromosomes, including the enzymes for replication and transcription. ...
... holding the DNA in place. This structure allows the long DNA molecules on the nucleus to be condensed into a much smaller space. Together, the histones form ‘beads’. However, there are also other proteins present in the chromosomes, including the enzymes for replication and transcription. ...
Study Guide for LS
... - Rosalind Franklin was able to create images of DNA molecules and discover that DNA was spiral shaped. ...
... - Rosalind Franklin was able to create images of DNA molecules and discover that DNA was spiral shaped. ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... A. Definition-use of organisms to perform practical tasks for humans B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic material D. Human genome project– a project aimed at sequen ...
... A. Definition-use of organisms to perform practical tasks for humans B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic material D. Human genome project– a project aimed at sequen ...
DNA Connection
... Line up of Genes • 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the human body. • Chromosomes are made of many genes joined together like beads on a string. ...
... Line up of Genes • 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the human body. • Chromosomes are made of many genes joined together like beads on a string. ...
What are the three steps in PCR?
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
Unit 1 Rev 2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enzymes that a cell makes are crucial for the cell to properly work, what does the cell have (use) in order to help it build thes ...
... ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enzymes that a cell makes are crucial for the cell to properly work, what does the cell have (use) in order to help it build thes ...
Name - EdWeb
... 12. If you stretched the DNA from a cell out, how long would it be? ____________________________ 13. How many chromosomes are in a human cell? _________in a mosquito? ________ a carp? _________ What is a protein? 14. How is a protein like a car engine? _______________________________________________ ...
... 12. If you stretched the DNA from a cell out, how long would it be? ____________________________ 13. How many chromosomes are in a human cell? _________in a mosquito? ________ a carp? _________ What is a protein? 14. How is a protein like a car engine? _______________________________________________ ...
Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn McCarty 1928
... transformation still took place Took an RNA destoying enzyme and transformation still took place ...
... transformation still took place Took an RNA destoying enzyme and transformation still took place ...
Reading Guide
... 5. Draw the AT base pair and indicate hydrogen bonding. Do the same for the GC base pair. 6. Describe “typical” DNA (B-DNA form) in terms of its major features. How is A-DNA different? 7. What is the major structural difference between a nucleotide and a deoxynucleotide? What is the major structural ...
... 5. Draw the AT base pair and indicate hydrogen bonding. Do the same for the GC base pair. 6. Describe “typical” DNA (B-DNA form) in terms of its major features. How is A-DNA different? 7. What is the major structural difference between a nucleotide and a deoxynucleotide? What is the major structural ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.