Genetics Science Learning Center
... 6. A DNA strand is made of ________________________ which make up ___________________ which make up sentences. 7. These "sentences" are called _________________________________________________________ Hint - Look at the navigation bar at the top, you'll need to click on "What is a Gene" to continue. ...
... 6. A DNA strand is made of ________________________ which make up ___________________ which make up sentences. 7. These "sentences" are called _________________________________________________________ Hint - Look at the navigation bar at the top, you'll need to click on "What is a Gene" to continue. ...
Introduction
... life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determining the characteristic of an organism. The DNA molecule is arranged as a double helix, whic ...
... life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determining the characteristic of an organism. The DNA molecule is arranged as a double helix, whic ...
... dna replication is necessary for the transmission of genetic information and thus such a process must achieve accurate copying of the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast l ...
Biology, Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Study Guide 1. What two
... 18. How can DNA with only 4 bases code for proteins made up of 20 different amino acids? 20. Translate a given mRNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. ...
... 18. How can DNA with only 4 bases code for proteins made up of 20 different amino acids? 20. Translate a given mRNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 10. A _______ is a section of DNA on a chromosome which carries hereditary information. 11. A _____________________ is found in the nucleus and contains genes. 12. The process in which DNA molecules form exact copies of themselves is _____________________. 13. The shape of the DNA can be described a ...
... 10. A _______ is a section of DNA on a chromosome which carries hereditary information. 11. A _____________________ is found in the nucleus and contains genes. 12. The process in which DNA molecules form exact copies of themselves is _____________________. 13. The shape of the DNA can be described a ...
Genetics
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet Genetics and Biotechnology Vocabulary
... - What is selective breeding? Genetic Engineering/Recombinant DNA? Gene Therapy? - What is one positive and one negative effect these technologies have had on our society and the ...
... - What is selective breeding? Genetic Engineering/Recombinant DNA? Gene Therapy? - What is one positive and one negative effect these technologies have had on our society and the ...
C13 Genetic Engineering
... Cutting DNA into pieces is done with restriction enzymes. Each one cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides. Separating DNA can be achieved by using gel electrophoresis. In DNA electrophoresis, the DNA cut with restriction enzymes is put into the well at one end (negative end – black) of the g ...
... Cutting DNA into pieces is done with restriction enzymes. Each one cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides. Separating DNA can be achieved by using gel electrophoresis. In DNA electrophoresis, the DNA cut with restriction enzymes is put into the well at one end (negative end – black) of the g ...
Ch. 15
... • 3. DNA polymerase copies the region between the primers. These copies then serve as templates to make more copies. • 4. In this way, just a few dozen cycles of replication can produce billions of copies of the DNA between the primers. ...
... • 3. DNA polymerase copies the region between the primers. These copies then serve as templates to make more copies. • 4. In this way, just a few dozen cycles of replication can produce billions of copies of the DNA between the primers. ...
word play - Discovery Education
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
DNA openbook assignment
... 3) State two words to describe a DNA molecule shape? ___________ __________ 4) In which organelle in the cell does the DNA exist? ____________________ 5) DNA in human cells is wound up into 23 pairs of ____________________ 6) Which of the bases in number 1 pair together? ____ / ____ and ____ / ___ 7 ...
... 3) State two words to describe a DNA molecule shape? ___________ __________ 4) In which organelle in the cell does the DNA exist? ____________________ 5) DNA in human cells is wound up into 23 pairs of ____________________ 6) Which of the bases in number 1 pair together? ____ / ____ and ____ / ___ 7 ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... * In separating DNA by Gel, why is size and not charge important in analyzing the results? ...
... * In separating DNA by Gel, why is size and not charge important in analyzing the results? ...
Some No-Nonsense Facts on
... information is used as a "blueprint" or set of instructions for building and maintaining a living creature. These instructions are found within almost all cells (the "internal" part), they are written in a coded language (the genetic code in DNA), they are copied at the time of cell division or repr ...
... information is used as a "blueprint" or set of instructions for building and maintaining a living creature. These instructions are found within almost all cells (the "internal" part), they are written in a coded language (the genetic code in DNA), they are copied at the time of cell division or repr ...
UTACCEL 2010
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA`s
... Maurice Wilkins showed James Watson some of Rosalind Franklin's x-ray crystallography images without asking her permission. Watson and Crick used these images to work out the structure of DNA. Was Wilkins right to share the images? Evaluate his decision (this means look at both sides of the argument ...
... Maurice Wilkins showed James Watson some of Rosalind Franklin's x-ray crystallography images without asking her permission. Watson and Crick used these images to work out the structure of DNA. Was Wilkins right to share the images? Evaluate his decision (this means look at both sides of the argument ...
DNA -- The Double Helix
... particular protein which in turn codes for a trait. For example, it may be the gene for baldness or the gene for blue eyes. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick established the structure of DNA. The shape of DNA is a double helix, which is like a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made o ...
... particular protein which in turn codes for a trait. For example, it may be the gene for baldness or the gene for blue eyes. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick established the structure of DNA. The shape of DNA is a double helix, which is like a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made o ...
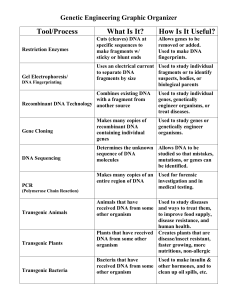
DNA Technology Tools Graphic Organizer KEY
... to separate DNA fragments or to identify fragments by size suspects, bodies, or biological parents ...
... to separate DNA fragments or to identify fragments by size suspects, bodies, or biological parents ...
2-3 DNA to Proteins - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... nucleotides pair up to form ladder rungs. There are four types: Adenine (A) goes with Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) goes with Guanine (G). The ladder shape then twists to form a helix. Copying – DNA can unzip and then new nucleotides attach to each side of the original. In the end you end up with two ne ...
... nucleotides pair up to form ladder rungs. There are four types: Adenine (A) goes with Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) goes with Guanine (G). The ladder shape then twists to form a helix. Copying – DNA can unzip and then new nucleotides attach to each side of the original. In the end you end up with two ne ...
Micro Quiz #3R Stu F2011 - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... E. Temperature dependent upon whether it is from a prokaryote or eukaryote 5. In prokaryotes, the enzyme that introduces negative supercoils into DNA by making doublestranded cuts is called: A. DNA gyrase B. RNA polymerase C. DNA polymerase D. Topoisomerase I E. DNA twistase ...
... E. Temperature dependent upon whether it is from a prokaryote or eukaryote 5. In prokaryotes, the enzyme that introduces negative supercoils into DNA by making doublestranded cuts is called: A. DNA gyrase B. RNA polymerase C. DNA polymerase D. Topoisomerase I E. DNA twistase ...
Genetics
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.