Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eu ...
... 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eu ...
DNA technology
... • Growth hormone deficiency – Faulty pituitary and regulation – Had to rely on cadaver source – Now easily produced by bacteria ...
... • Growth hormone deficiency – Faulty pituitary and regulation – Had to rely on cadaver source – Now easily produced by bacteria ...
13-3 Cell Transformation
... What is Transformation? Transformation = cell takes in DNA from outside the cell The external DNA becomes a component of the cell’s DNA ...
... What is Transformation? Transformation = cell takes in DNA from outside the cell The external DNA becomes a component of the cell’s DNA ...
Cloze passage 4
... CLOZE PASSAGE No 4 Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 ...
... CLOZE PASSAGE No 4 Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics Test Review
... pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
... pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
name period ______ date
... 3. What is the name of the enzyme that breaks the nitrogen bases apart to get them ready for replication? 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the co ...
... 3. What is the name of the enzyme that breaks the nitrogen bases apart to get them ready for replication? 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the co ...
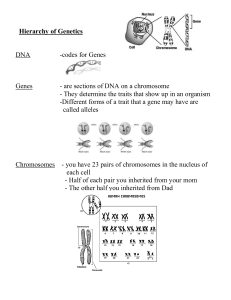
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
HomeworkCh7
... For Chapter 7 on separate sheets of paper 1. Draw the four nucleotides of DNA a. label the 5’ and 3’ carbons 2. Draw a chain of connected nucleotides 4-5 long, and the complement strand in the correct orientation. Show the following important features of DNA: a. hydrogen bonding that keeps them toge ...
... For Chapter 7 on separate sheets of paper 1. Draw the four nucleotides of DNA a. label the 5’ and 3’ carbons 2. Draw a chain of connected nucleotides 4-5 long, and the complement strand in the correct orientation. Show the following important features of DNA: a. hydrogen bonding that keeps them toge ...
Biology Molecular Genetic Review
... 15. Why do only a specific amino acid attach to each transfer RNA? ...
... 15. Why do only a specific amino acid attach to each transfer RNA? ...
PCR - University of Hawaii
... • AMV reverse transcriptase from the avian myeloblastosis virus • Reverse Transcriptase (RT): A DNA polymerase enzyme that uses an RNA template to synthesize a complementary molecule of double stranded DNA • RNA template ...
... • AMV reverse transcriptase from the avian myeloblastosis virus • Reverse Transcriptase (RT): A DNA polymerase enzyme that uses an RNA template to synthesize a complementary molecule of double stranded DNA • RNA template ...
Chapter 10
... The following is a list of the main themes covered in this chapter and some study objectives. As you study, focus on these areas. Understand how the information you study fits into these themes and how these themes relate to each other. Be sure you master each objective before moving on. 1. Various ...
... The following is a list of the main themes covered in this chapter and some study objectives. As you study, focus on these areas. Understand how the information you study fits into these themes and how these themes relate to each other. Be sure you master each objective before moving on. 1. Various ...
DNA and Genetic Engineering Midterm Review Chapter 12 Review
... 13. The condition in which cells have many sets of chromosomes; it may instantly produce new plant species that are larger and stronger. 16. Gel electrophoresis enables scientists to separate and analyze DNA fragments, to compare genomes of different individuals and organisms, and to identify a spec ...
... 13. The condition in which cells have many sets of chromosomes; it may instantly produce new plant species that are larger and stronger. 16. Gel electrophoresis enables scientists to separate and analyze DNA fragments, to compare genomes of different individuals and organisms, and to identify a spec ...
Journey Into dna
... The human genome is comprised of two sets of ________ chromosomes. About _______% of the genome consists of sequences that have no known ...
... The human genome is comprised of two sets of ________ chromosomes. About _______% of the genome consists of sequences that have no known ...
DNA experiments exercise
... What do these data reveal about the ratios different bases? Watson and Crick used this information as one of their key insights into the double helix structure of DNA. ...
... What do these data reveal about the ratios different bases? Watson and Crick used this information as one of their key insights into the double helix structure of DNA. ...
What`s the Big Deal About DNA?
... 1. Describe what DNA looks like, or draw a picture in the space provided. What is a double helix? What do the letters A, T, C, and G stand for? ...
... 1. Describe what DNA looks like, or draw a picture in the space provided. What is a double helix? What do the letters A, T, C, and G stand for? ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.