DNA Worksheet
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
... Describe the basic structure (double helix, sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA, and describe its function in genetic inheritance. What is DNA: http://www.statedclearly.com/what-is-dna/ ...
... Describe the basic structure (double helix, sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA, and describe its function in genetic inheritance. What is DNA: http://www.statedclearly.com/what-is-dna/ ...
Test Study Guide
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
Genetic Engineering
... Positive mutations desirable characteristics; can be increased by ____________, ____________, etc. (ex: seedless oranges) ...
... Positive mutations desirable characteristics; can be increased by ____________, ____________, etc. (ex: seedless oranges) ...
Microbiology Unit 3 Study Guide
... 3. What are the DNA base pair rules? 4. How would you transcribe the following DNA sequence? ATA CGT CAT AAG 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for ...
... 3. What are the DNA base pair rules? 4. How would you transcribe the following DNA sequence? ATA CGT CAT AAG 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found ...
... 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found ...
AT CG - Middletown Public Schools
... DNA and Mutations DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. B ...
... DNA and Mutations DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. B ...
Genetic Changes = Mutations
... c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickle cell anemia is an example of a disease caused by this very tiny DNA error 8. Frameshift mutation: a. a single base is added or deleted in the DNA sequence b. resulting in every amino ac ...
... c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickle cell anemia is an example of a disease caused by this very tiny DNA error 8. Frameshift mutation: a. a single base is added or deleted in the DNA sequence b. resulting in every amino ac ...
Name: Genetics Study Guide
... What does codominance mean in genetics? How is it different from Incomplete dominance? Know the difference between a hybrid and a purebred. In what decade was the DNA structure discovered? Who discovered the structure of DNA? What is the scientific name of the DNA structure? Which is the correct ord ...
... What does codominance mean in genetics? How is it different from Incomplete dominance? Know the difference between a hybrid and a purebred. In what decade was the DNA structure discovered? Who discovered the structure of DNA? What is the scientific name of the DNA structure? Which is the correct ord ...
SW describe how techniques such as DNA
... differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
... differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
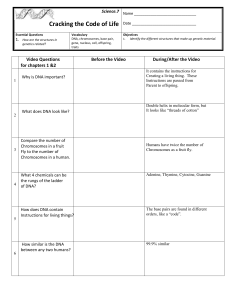
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... During/After the Video It contains the instructions for Creating a living thing. These Instructions are passed from Parent to offspring. ...
... During/After the Video It contains the instructions for Creating a living thing. These Instructions are passed from Parent to offspring. ...
4.1 Le Noyau
... result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
... result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
jeopardy honors DNA 12-1 thru 12-4 only
... genetic variation. If something is a beneficial mutation, it may increase over time in the population (change over time). ...
... genetic variation. If something is a beneficial mutation, it may increase over time in the population (change over time). ...
DNA - VanityWolveriine
... encoded in the sequence of the bases and is transcribed as the strands unwind and replicate.” ...
... encoded in the sequence of the bases and is transcribed as the strands unwind and replicate.” ...
notes
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
Name:
... 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? 12. What amino acid does the CAG codon code for? 13. What is the first codon in all mRNA sequences? 14. What transports the amino acids to the ribosome during translation? ...
... 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? 12. What amino acid does the CAG codon code for? 13. What is the first codon in all mRNA sequences? 14. What transports the amino acids to the ribosome during translation? ...
Document
... RNA that is located in the germ plasma usually on a chromosome and that is the functional unit of inheritance controlling the transmission and expression of one or more traits. ...
... RNA that is located in the germ plasma usually on a chromosome and that is the functional unit of inheritance controlling the transmission and expression of one or more traits. ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.