* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.1 Le Noyau
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
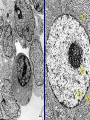
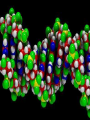
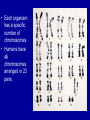
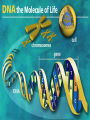
4.1 The nucleus A trait- particular feature The nucleus • Responsible for heredity and for controlling the functions of the cell. • heredity = the process through which patterns of traits are pased on from an individual to it offspring • Information in the nucleus determines your traits • This information also determines: – The type of cell – Its function – Its growth – When it will divide( reproduce) – When it will die DNA • Deoxyribonucleic acid Made of 4 nitrogen bases Adenine(A) Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) • Everything that occurs within a cell is the result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule • When a cell is ready to divide, each strand of loosely coiled DNA folds up further into a very compact, xshaped structure called a chromosome. • Each organism has a specific number of chromosomes. • Humans have 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs. 20 60 78 80 44 Genes are small segments of DNA located at specific places on the chromosome. The difference between a gene and a chromosome? • Genes can be composed of hundreds or thousands nitrogen bases. • Produces a particular trait. • Each chromosome is made up of thousands of genes. • Therefore, can produce thousands of traits.