DNA Cloning - MrMsciences
... • a line of genetically identical cells or individuals derived from a single ancestor • produces many copies of a piece of DNA • uses a little fraction as gene of interest • cultivates a large amount for studying functions ...
... • a line of genetically identical cells or individuals derived from a single ancestor • produces many copies of a piece of DNA • uses a little fraction as gene of interest • cultivates a large amount for studying functions ...
File - Chereese Langley
... 2006, it was shown that this rule applies to four of the five types of double stranded genomes; specifically it applies to the eukaryotic chromosomes, the bacterial chromosomes, the double stranded DNA viral genomes, and the archival chromosomes. ...
... 2006, it was shown that this rule applies to four of the five types of double stranded genomes; specifically it applies to the eukaryotic chromosomes, the bacterial chromosomes, the double stranded DNA viral genomes, and the archival chromosomes. ...
DNA extraction activity
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
Molecular Techniques in Cell & Molecular Biology
... They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specific gene products such as human insulin in bacteria. (We offer a full-semester course in RDNA techniques; this is by necessity a brief intro) 4 steps: 1. Recombination 2. Sel ...
... They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specific gene products such as human insulin in bacteria. (We offer a full-semester course in RDNA techniques; this is by necessity a brief intro) 4 steps: 1. Recombination 2. Sel ...
What is the NUTRIENT needed for growth and repair
... Exponential increase in the amount of DNA produced in PCR ...
... Exponential increase in the amount of DNA produced in PCR ...
DNA Structure and Function
... Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Sickle-cell anemia is an inherited disease that affects red blood cells. In people who have this disease, one amino acid is substituted for another amino acid in a blood protein. What causes sickle-cell anemia? p153 ...
... Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Sickle-cell anemia is an inherited disease that affects red blood cells. In people who have this disease, one amino acid is substituted for another amino acid in a blood protein. What causes sickle-cell anemia? p153 ...
Simon Rasmussen Assistant professor CBS
... • DNA can be amplified using Polymerase Chain Reaction DNA is often found in very low amounts (eg. 1 ug) ...
... • DNA can be amplified using Polymerase Chain Reaction DNA is often found in very low amounts (eg. 1 ug) ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
... Name the enzyme involved in protein synthesis which manufactures mRNA using DNA as a template. DNA polymerase ...
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
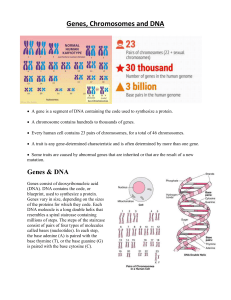
... A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or ...
... A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... molecule? What kind of bond holds the two chains of the double helix together? 9. When is DNA replicated? 10. Understand Messelsen-Stahl’s experiment. 11. What does “semi-conservative” replication mean? 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between ...
... molecule? What kind of bond holds the two chains of the double helix together? 9. When is DNA replicated? 10. Understand Messelsen-Stahl’s experiment. 11. What does “semi-conservative” replication mean? 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between ...
Graduate Program in Molecular Cell Biology:
... Limited number of places YES, number of places 6, registration necessary YES For registration or questions please contact 9003 70407; [email protected] Aim: A short introduction into specific molecular biological approaches and working techniques to be trained in theory and practice. Descr ...
... Limited number of places YES, number of places 6, registration necessary YES For registration or questions please contact 9003 70407; [email protected] Aim: A short introduction into specific molecular biological approaches and working techniques to be trained in theory and practice. Descr ...
DNA-drug interactions and charge transfer processes in DNA.
... Some organic molecules can bind to DNA and thus interfere with DNA replication, transcription and gene expression process, or even direct nucleic acid cleavage. These small molecules can thus act as therapeutic agents in cancer cure. These drug molecules can bind to DNA by different mechanisms. The ...
... Some organic molecules can bind to DNA and thus interfere with DNA replication, transcription and gene expression process, or even direct nucleic acid cleavage. These small molecules can thus act as therapeutic agents in cancer cure. These drug molecules can bind to DNA by different mechanisms. The ...
Outline
... Why did many researchers originally believe that genes were probably made of protein? As you know, all amino acids contain an NH2 group...why couldn't Hershey and Chase have used radioactive nitrogen instead of radioactive sulfur to track the bacteriophage protein? Why is it important to the o ...
... Why did many researchers originally believe that genes were probably made of protein? As you know, all amino acids contain an NH2 group...why couldn't Hershey and Chase have used radioactive nitrogen instead of radioactive sulfur to track the bacteriophage protein? Why is it important to the o ...
13-2 Manipulating DNA
... 5) Used to locate and identify a particular genes or used to compare individuals. Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, and to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. ...
... 5) Used to locate and identify a particular genes or used to compare individuals. Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, and to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. ...
Biology Ch. 12 Vocab
... 11. group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon ...
... 11. group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... The Sugar is a ______Carbon Sugar called ___________________________ To each Deoxyribose, there is a _____________________________________ connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
... The Sugar is a ______Carbon Sugar called ___________________________ To each Deoxyribose, there is a _____________________________________ connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... A gene – what is it? • It is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. Genes are found in our chromosomes, which parents pass on to offspring in their sex cells in reproduction. Different versions of the same gene are called alleles and these can determine features like eye colour and the ...
... A gene – what is it? • It is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. Genes are found in our chromosomes, which parents pass on to offspring in their sex cells in reproduction. Different versions of the same gene are called alleles and these can determine features like eye colour and the ...
Jeopardy - Grayslake Central High School
... a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
... a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.