DNA-notes
... (Each gene has its own specific location called a LOCUS) *Double stranded, double helix shape ...
... (Each gene has its own specific location called a LOCUS) *Double stranded, double helix shape ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
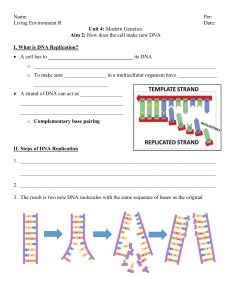
... I. DNA A. DNA- a chemical that contains information an organism needs to grow and function 1. Watson and Crick made and accurate model of DNA in 1953 2. The structure of DNA is similar to a twisted ladder. a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder ...
... I. DNA A. DNA- a chemical that contains information an organism needs to grow and function 1. Watson and Crick made and accurate model of DNA in 1953 2. The structure of DNA is similar to a twisted ladder. a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder ...
Biology Packet 7: DNA & RNA
... Explain the function of DNA. Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of ...
... Explain the function of DNA. Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of ...
DNA Test Review
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
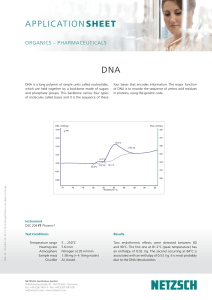
Application Sheet: DNA - NETZSCH Thermal Analysis
... NGB ∙ AS ∙ 135-2006 ∙ EN ∙ 07/13 ∙ Technical specifications are subject to change. ...
... NGB ∙ AS ∙ 135-2006 ∙ EN ∙ 07/13 ∙ Technical specifications are subject to change. ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 3 Say if the following variations are inherited or acquired. (a) freckles _____________________________________ (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clo ...
... 3 Say if the following variations are inherited or acquired. (a) freckles _____________________________________ (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clo ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic Organisms – Contain genes from other organisms – Usually bacteria because they reproduce rapidly and are easy to grow. ...
... Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic Organisms – Contain genes from other organisms – Usually bacteria because they reproduce rapidly and are easy to grow. ...
DO NOW
... Why does the leading strand form continuously while the lagging strand is formed in fragments? ...
... Why does the leading strand form continuously while the lagging strand is formed in fragments? ...
5. Protein Synthesis
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
WS 12 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with ____, and C bonds with _____. This is due to ___________________ bonding. A and T form ______ hydrogen bonds, C and G form ______ hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and __________. ...
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with ____, and C bonds with _____. This is due to ___________________ bonding. A and T form ______ hydrogen bonds, C and G form ______ hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and __________. ...
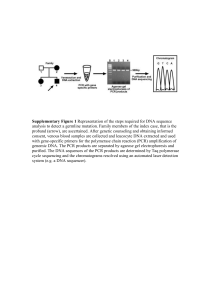
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Vocabulary 7
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
DNA, Genes and Chromosomes
... model in a flow diagram showing the progression from a cell to a gene writing descriptions. 3. A distinction will be achieved if you produce a poster writing a summary about how genes can be shuffled during sexual reproduction. ...
... model in a flow diagram showing the progression from a cell to a gene writing descriptions. 3. A distinction will be achieved if you produce a poster writing a summary about how genes can be shuffled during sexual reproduction. ...
So You Think
... ________________ 9. Translation (the making of proteins) happens at this organelle. ...
... ________________ 9. Translation (the making of proteins) happens at this organelle. ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.