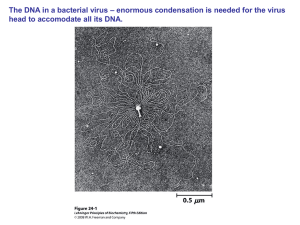
ap: chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 16. Describe the “priming of the DNA” before replication. _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 17. List some of the steps involved in DNA repair. _________ ...
... 16. Describe the “priming of the DNA” before replication. _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 17. List some of the steps involved in DNA repair. _________ ...
Slide 1
... molecule is half old DNA and half new (one strand is from the original molecule and one strand is newly synthesized using the old strand as a template). ...
... molecule is half old DNA and half new (one strand is from the original molecule and one strand is newly synthesized using the old strand as a template). ...
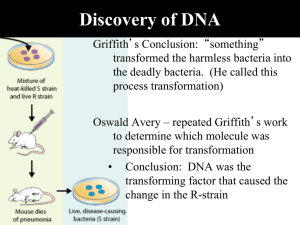
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
DNA * History, Structure, and Functions
... happen if he crossed various pea plants He would carefully transfer the pollen from one plant to another He did this thousands of times ...
... happen if he crossed various pea plants He would carefully transfer the pollen from one plant to another He did this thousands of times ...
a10c Biotechnology
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
MolecularBiology1APLab6
... • Enzymes that cut DNA at very specific base sequences (often palindromes) • Make blunt or sticky ends • Evolved to combat invasive DNA from viruses • Does not cut bacterium’s DNA because it’s missing correct DNA sequence • Different bacterial strains have different RE ...
... • Enzymes that cut DNA at very specific base sequences (often palindromes) • Make blunt or sticky ends • Evolved to combat invasive DNA from viruses • Does not cut bacterium’s DNA because it’s missing correct DNA sequence • Different bacterial strains have different RE ...
Manipulating DNA - Lemon Bay High School
... How are changes made to DNA? • Scientists use their knowledge of the structure of DNA and its chemical properties to study and change DNA molecules. • Making changes in the DNA code of a living organism ...
... How are changes made to DNA? • Scientists use their knowledge of the structure of DNA and its chemical properties to study and change DNA molecules. • Making changes in the DNA code of a living organism ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... Click on the link that says “Tour the basics”. A new window will open, you can navigate sections by using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four b ...
... Click on the link that says “Tour the basics”. A new window will open, you can navigate sections by using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four b ...
12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
Worksheet for 4/16
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
Slide 1
... In mitosis both helices attach to each other at the centromere forming sister chromatids….which makes the X-shaped chromosome you normally think of when thinking about chromosomes. The kinetochore is a complex of proteins formed at the centromere to binds the mitotic spindle….thus allowing sister ch ...
... In mitosis both helices attach to each other at the centromere forming sister chromatids….which makes the X-shaped chromosome you normally think of when thinking about chromosomes. The kinetochore is a complex of proteins formed at the centromere to binds the mitotic spindle….thus allowing sister ch ...
Virtual DNA Lab
... 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called the instruction manual for our body? _______________________________ __________ ...
... 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called the instruction manual for our body? _______________________________ __________ ...
Players in the protein game
... proteins. They are built inside cells using Dna code however it folds that’s the what it does. ...
... proteins. They are built inside cells using Dna code however it folds that’s the what it does. ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen bonds 9. You have separated the nucleotides in a piece of DNA ...
... 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen bonds 9. You have separated the nucleotides in a piece of DNA ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... * Develop and use models at different scales to explain the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to offspring. * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subs ...
... * Develop and use models at different scales to explain the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to offspring. * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subs ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.