2D Barcode Quiz
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
AZBio Ch 13
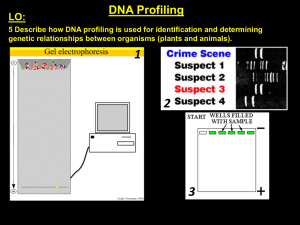
... •DNA fragments are poured onto a gel •Electric voltage moves the DNA fragments across the gel •Because longer segments move across the gel more slowly, and do not go as far •Based on size, the DNA fragments make a pattern of bands on the gel ...
... •DNA fragments are poured onto a gel •Electric voltage moves the DNA fragments across the gel •Because longer segments move across the gel more slowly, and do not go as far •Based on size, the DNA fragments make a pattern of bands on the gel ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... A viral vector is used to transfer bacterial DNA into another bacteria either through a prophage & Lysogenic Cycle or through the lytic cycle. What is this process ...
... A viral vector is used to transfer bacterial DNA into another bacteria either through a prophage & Lysogenic Cycle or through the lytic cycle. What is this process ...
Why is DNA called the "blueprint of life"?
... 3.1.B.B1.a, 3.1.B.B1.b, 3.1.B.B3.b, 3.1.B.B5.c, 3.1.B.B5.d, ...
... 3.1.B.B1.a, 3.1.B.B1.b, 3.1.B.B3.b, 3.1.B.B5.c, 3.1.B.B5.d, ...
Genetics
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
Study Guide- DNA, Protein Synthesis, Mitosis and Meiosis
... Study Guide- DNA, Protein Synthesis, Mitosis and Meiosis 1) Outline the scientists and the experiments that lead to the discovery of DNA, and later, it’s structure. Include: Meischer, Griffith, Avery, Hershey and Chase, Watson and Crick and Rosalind Franklin. 2) Discuss the structure and chemical co ...
... Study Guide- DNA, Protein Synthesis, Mitosis and Meiosis 1) Outline the scientists and the experiments that lead to the discovery of DNA, and later, it’s structure. Include: Meischer, Griffith, Avery, Hershey and Chase, Watson and Crick and Rosalind Franklin. 2) Discuss the structure and chemical co ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 6. What is it with the structure of DNA that allows it to store so much information?_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Part Two: DNA Replication 7. Where does DNA replication take place:__________________ 8. When does DNA replication take place:_________ ...
... 6. What is it with the structure of DNA that allows it to store so much information?_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Part Two: DNA Replication 7. Where does DNA replication take place:__________________ 8. When does DNA replication take place:_________ ...
Modeling DNA
... Bonus: Your DNA model holds its double-helix shape, without your intervention, when your teacher comes to check it. ...
... Bonus: Your DNA model holds its double-helix shape, without your intervention, when your teacher comes to check it. ...
: Determining DNA sequences
... – Plasmid Vectors: help insert the DNA fragment that needs cloned into a host cell. Inside the host cell both the vector and the DNA fragment are cloned (copied). In the example a DNA fragment is inserted into the plasmid. The plasmid is then inserted into the host cells and produces many copies of ...
... – Plasmid Vectors: help insert the DNA fragment that needs cloned into a host cell. Inside the host cell both the vector and the DNA fragment are cloned (copied). In the example a DNA fragment is inserted into the plasmid. The plasmid is then inserted into the host cells and produces many copies of ...
1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule
... 1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule. Include in your explanation the words and phrases: base-pairing rule, complementary nucleotides, cytoplasm, DNA, gene, messenger RNA, nucleotide, nucleus, RNA polymerase, amino acid, anti-codon, codon, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, nucleotide, ...
... 1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule. Include in your explanation the words and phrases: base-pairing rule, complementary nucleotides, cytoplasm, DNA, gene, messenger RNA, nucleotide, nucleus, RNA polymerase, amino acid, anti-codon, codon, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, nucleotide, ...
WEEK 1 PROBLEMS Problems From Chapter 1
... 1.2 When the base composition of a DNA sample from Micrococcus luteus was determined, 37.5 percent of the bases were found to be cytosine. The DNA of this organism is known to be double-stranded. What is the percentage of adenine in this DNA? 1.3 DNA extracted from a certain virus has the following ...
... 1.2 When the base composition of a DNA sample from Micrococcus luteus was determined, 37.5 percent of the bases were found to be cytosine. The DNA of this organism is known to be double-stranded. What is the percentage of adenine in this DNA? 1.3 DNA extracted from a certain virus has the following ...
Lect2 Genetics
... DNA repair mechanisms Recombination can occur –cutting out and insertion of pieces of DNA These can all leads to changes in genetic material and thus changes in phenotype! ...
... DNA repair mechanisms Recombination can occur –cutting out and insertion of pieces of DNA These can all leads to changes in genetic material and thus changes in phenotype! ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... DNA can make a copy of it itself BECAUSE of the way the bases pair up ...
... DNA can make a copy of it itself BECAUSE of the way the bases pair up ...
Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
... Finally we would lite to know if you have heard about the recent discoveries of Encode? Some months ago a new explanation of DNA was discovered :it solves and sheds light on diseases as cancer or Alzheimer’s and on others ailment diseases. Since the beginning of researches about the human genome, sc ...
... Finally we would lite to know if you have heard about the recent discoveries of Encode? Some months ago a new explanation of DNA was discovered :it solves and sheds light on diseases as cancer or Alzheimer’s and on others ailment diseases. Since the beginning of researches about the human genome, sc ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... A gene is a sequence of ____ DNA on a chromosome ___________ that codes for one protein ________. **Remember, not all of the ____ DNA codes for proteins. The parts that do are called ______, genes the parts that don’t are called non-coding regions ___________________. ...
... A gene is a sequence of ____ DNA on a chromosome ___________ that codes for one protein ________. **Remember, not all of the ____ DNA codes for proteins. The parts that do are called ______, genes the parts that don’t are called non-coding regions ___________________. ...
Laboratory Exam I - HCC Learning Web
... What is the difference between xylem and phloem? What color of the visible light spectrum is the least effective in photosynthesis (it is not absorbed)? What is paper chromatography? What is the basis of fractionation (there are 3 possible answer choices)? Which pigment acts as the reaction center m ...
... What is the difference between xylem and phloem? What color of the visible light spectrum is the least effective in photosynthesis (it is not absorbed)? What is paper chromatography? What is the basis of fractionation (there are 3 possible answer choices)? Which pigment acts as the reaction center m ...
Genetic Engineering
... 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of individuals to get the best characteristics of both. ...
... 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of individuals to get the best characteristics of both. ...
The purines In DNA, the pyrimidine bases are
... 1. Purine bases that are consumed in the human diet in the form of DNA or RNA are mostly excreted in the form of uric acid. Xanthine oxidase catalyzes this formation of uric acid from purine bases. 2. The use of tetrahydrofolic acid (TFA) by several of the enzymes in purine and pyrimidine synthesis ...
... 1. Purine bases that are consumed in the human diet in the form of DNA or RNA are mostly excreted in the form of uric acid. Xanthine oxidase catalyzes this formation of uric acid from purine bases. 2. The use of tetrahydrofolic acid (TFA) by several of the enzymes in purine and pyrimidine synthesis ...
Hershey and Chase`s Experiment
... They adhere to the surface of the bacteria and inject their DNA into the bacteria. Their DNA codes for the assembly of more phages after their DNA is incorporated into the bacterial chromosome. Hershey and Chase Experiments ...
... They adhere to the surface of the bacteria and inject their DNA into the bacteria. Their DNA codes for the assembly of more phages after their DNA is incorporated into the bacterial chromosome. Hershey and Chase Experiments ...
Slide 1
... the start of the target genes. 3. DNA Polymerase replicates the DNA using complementary base pairing. 4. This cycle is repeated many times, until there are thousands of copies – enough to amplify even tiny samples found at a crime scene! ...
... the start of the target genes. 3. DNA Polymerase replicates the DNA using complementary base pairing. 4. This cycle is repeated many times, until there are thousands of copies – enough to amplify even tiny samples found at a crime scene! ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.