* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ws: Cell Membrane, The Gatekeeper
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
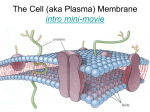
Biology Jones Name: Period: Date: Cell Membrane…”The Gate Keeper” Color the diagram of the cell membrane. A. Protein channel (color all proteins the same) B. Carbohydrate chains C. Phospholipid head D. Phospholipid tails E. Cholesterol C. D. B. E. A. A. Use your macromolecule notes and your cell membrane notes to answer the following questions. 1. What molecule makes up the majority of the cell membrane? ______________________________ 2. What are the monomers to the molecule in answer #1? ___________________________________ 3. Draw a phospholipid and label the polar and non-polar regions. 4. What does it mean to be a polar molecule? 5. Other than the hydrophilic component of the phospholipid, what is another example of a polar molecule that we have discussed in class? _____________________ 6. What does hydrophilic mean? 7. What does hydrophobic mean? 8. How do phospholipids interact with water to form the phospholipid bilayer? 9. What types of molecules can slide across the phospholipids? What characteristics allow them the move in and out the cell this way? 10. How do molecules get into the cell if they cannot slide across the phospholipids? What types of molecules get in this way? What characteristics force these molecules to get into the cell this way? 11. How do the proteins stay anchored in the cell membrane? 12. What is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane? 13. What is the fluid mosaic model? In your answer include what component contributes to the “fluid” part and what component contributes to the “mosaic” part. 14. Structure and function: fill in the blank: The __________________________controls the internal environment of the cell by only allowing certain molecules to enter and exit the cell, so it is said to be _____________________________. Because it has two layers of lipids and proteins it is called a ________________________. The membrane can function as a gate keeper due to its structure. Cell membranes are mostly made of _____________________ each one with a head that is _____________________ and two tails that are _________________________. The head is water loving or _______________________ so they face the polar water inside and outside the cell. The tails are water fearing or ___________________ so they face away from the water and form the center of the bilayer. Because the tails of the phospholipids are non-polar, only small and _______________________ molecules can slide across them. The two primary molecules that get into the cell this way are _____________ and ________________. Even though it is polar, ____________ can very slowly slide across the phospholipids because it is so small. Molecules that are large and have a ______________ have to enter the cell through _____________________________.