* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
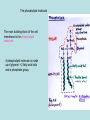
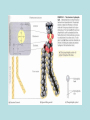
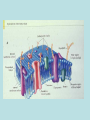
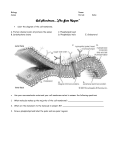
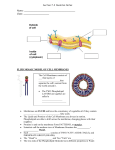
Cell Membrane Structure and Function The phospholipid molecule The main building block of the cell membrane is the phospholipid molecule. A phospholipid molecule is made up of glycerol + 2 fatty acid tails and a phosphate group. Phospholipid Molecule Polar head Non-polar tails A polar molecule ( or polar part of a molecule) is overall neutral, but it has an uneven distribution of electrons and so has oppositely charged areas. The polar head is hydrophilic and likes water molecules. hydro = water Philic = loving The fatty acid tails are hydrophobic and do not mix with water. Hydro = water Phobic = afraid of, dreads Do little activity http://telstar.ote.cmu.edu/Hughes/tutorial/cellme mbranes/orient2.swf…….. Structure of the membrane • Phospholipids: form a bilayer and are the main building blocks of the membrane. It has a very limited permeability. • Cholesterol: Binds to the phospholipids. Increases strength and restricts movement • Sugars: give signature, identify cell as self. Foreign invaders are identified by immune system. • Proteins: are the gatekeepers • Receptor sites for hormones ( chemical messengers) that turn activities on or off • Transport: passively or actively move things in or out across the membrane • Bind neighbouring cells together • Enzymes that take part in chemical reactions ( such as in the mitochondria or chloroplasts) • Aid in cell to cell communication