* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
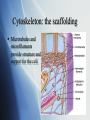
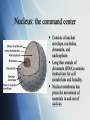
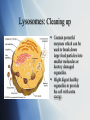
Cell Organelles The different structures of the cell Cell Wall: a rigid covering Rigid outer layer found in plant and bacteria cells. Provides protection from physical injury Provides skeletal support. Contains openings that make it totally permeable. Plasma Membrane: the fluid gate Composed of protein of lipid (fat) molecules. Acts as a boundary to contain cytoplasm Selectively permeable membrane to select chemicals that can pass in and out of cells. Cytoplasm: the medium for movement Jelly-like material that fills cells. Made mostly of water. Serves as a “molecular soup” in which organelles are suspended in. The medium for transport. Cytoskeleton: the scaffolding Microtubules and microfilaments provide structure and support for the cell. Nucleus: the command center Consists of nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin, and nucleoplasm Long thin strands of chromatin (DNA) contains instructions for cell metabolism and heredity. Nuclear membrane has pores for movement of materials in and out of nucleus. Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth & Rough Large workspace for the cell. “Rough” appearance due to the presence of ribosomes “Smooth” ER connected to Rough ER. Smooth ER has different functions for different cells. Storage of enzymes, and the production and storage of lipids. Mitochondria: Power packs Create ATP - the cell’s chemical energy. Can number from 1 to 1000’s inside eukaryotic cells. Folds in the Cristae increase the surface area for addition production of ATP’s Matrix inside contains hundreds of enzymes. Golgi Apparatus Mainly devoted to processing the proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Modifies the proteins for distribution. Lysosomes: Cleaning up Contain powerful enzymes which can be used to break down large food particles into smaller molecules or destroy damaged organelles. Might digest healthy organelles to provide the cell with extra energy. Vacuoles: Storage and packaging Membrane-bound sacs found in cytoplasm. Same type of material as the plasma membrane. Help in waste disposal, transport, storage, and growth. Much larger in plant cells. They aid in giving the plant cell support when filled with water. Also store important substances like salts, minerals, and nutrients. Contractile vacuoles are specialized to pump water out of the cell. Vesicles: transport carries Small vacuoles Usually formed at Golgi apparatus. Carry protein molecules to other organelles or the plasma membrane. Ribosome: the protein workbench Site of protein synthesis Found on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Inside the cell animation. Click here.