* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis Worksheet
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
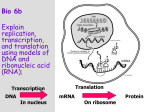
Protein Synthesis Worksheet Directions: 1. Use the DNA code to create your mRNA code. 2. Use the mRNA code to create your tRNA code. 3. Use the mRNA code to determine your amino acids (pay attention to sequence orientation!). 4. Answer any questions by circling the correct underlined answer. 1. 5’ T C C G C G C A G A G C T A G 3’ DNA mRNA tRNA 3’ 5’ 5’ 3’ Amino Acids 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. 5’ DNA A C A A G A G C G G T A C T G A 3’ mRNA 3’ tRNA Amino Acids 5’ 5’ 3’ 5. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 6. (mRNA/rRNA) is used to carry the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes. 7. (tRNA/rRNA) makes up the ribosome. 8. (DNA/RNA) uses uracil instead of thymine. 9. (RNA/amino) acids make up a protein. 10. 5’ DNA A T T G C T G T G G T A T G G G 3’ mRNA 3’ 5’ tRNA 5’ Amino Acids 11. Transcription takes place in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 12. tRNA is used in (translation/transcription). 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 3’ 20. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 21. (5’-3’/3’-5’) mRNA’s are read in this direction. 22. (large ribosome subunit/small ribosome subunit) Binds first with mRNA at the beginning of translation. 23. (large ribosomal subunit/MET tRNA) Second item to bind to the developing translation complex (after #22). 24. (A site/ P site/ E site) The location where a tRNA (and it’s amino acid) enter a ribosome. 25. (A site/ P site/ E site) The location where a growing polypeptide is transferred from. 26. (A site/ P site/ E site) The location where an empty tRNA exits the ribosome. 27. (Start codon/stop codon) When entering the A site, causes the ribosome and translation complex to dissociate. 28. (20/64/128) The number of possible codons using four nucleotides. 29. (20/64/128) The number of amino acids used for protein synthesis. 30. (redundancy/inaccuracy/inconsistency) Describes the occurrence of an amino acid being coded by more than one codon.