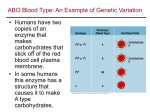
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download print last name first name
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
PRINT LAST NAME ___________________________ FIRST NAME ___________________________ SIGNATURE _________________________________ STUDENT ID# __________________________ BIOLOGY 1 Summer 2002 FINAL August 3, 2002 Professor Mel Green INSTRUCTIONS: There are 20 questions for a total of 400 points in this 2-hour exam. Each question is worth 25 points. Avoid using abbreviations unless otherwise indicated. No questions will be answered by TA’s during the exam!! By signing this waiver, I give permission for this exam to be left for me to pick up in the Humanities and Social Science building lower level West Wing, in the hall near room 1101. I realize this procedure may expose my grade to public scrutiny. I am also aware that unsigned exams can be picked up from Dr. Green. Signature _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ POINTS 1. ________________________________ 11. ________________________________ 2. ________________________________ 12. ________________________________ 3. ________________________________ 13. ________________________________ 4. ________________________________ 14. ________________________________ 5. ________________________________ 15. ________________________________ 6. ________________________________ 16. ________________________________ 7. ________________________________ 17. ________________________________ 8. ________________________________ 18. ________________________________ 9. ________________________________ 19. ________________________________ 10. ________________________________ 20. ________________________________ TOTAL __________________________ 1. Name and draw the following (in parts a-c) a. The two pyrimidines in DNA: _______________________ and _______________________ (Drawing the ring structure of a pyrimidine is fine) a. A molecule that increases the fluidity of membranes and is the precursor of all steroid hormones: _____________________________ (Drawing the ring structure is fine) b. The three-carbon product of glycolysis: ___________________________ c. What type(s) of R groups in amino acids makes proteins soluble: In membranes? _______________________________ In the cytoplasm?_____________________________ d. Name (don’t draw) the three basic amino acids found in proteins: _________________________, __________________________, _________________________ 2. Match by placing the best correct letter next to the appropriate number (letters may be used once, more than once, or not at all). a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum g. Bound Ribosomes b. Cytoskeleton h. Microtubules c. Free ribosomes i. Peroxisome d. Golgi apparatus j. Microfilament e. Mitochondria k. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum f. Lysosome l. Extracellular matrix (ECM) 1. 2. 3. 4. _____ Cilia and flagella are made out of this type of cytoskeleton fiber _____ Contains enzymes such as oxidase and catalase to break down fatty acids _____ Products of the ER are modified here by adding a sugar to the protein, thus directing it _____ Are attached to the ER, thus making products for export 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. _____ The main function is cellular support and shape _____ Cytoskeleton fiber used in muscle contraction _____ Membrane network that makes secretory proteins and membrane proteins _____ Contains enzymes that break down old denatured proteins and food particles _____ Animal cell organelle containing electron transport proteins _____ Contains fibronectins and integrins, function is support and anchorage to other cells 3. ATP is available for use to make a dipeptide from two component amino acids. Δ G0 for the hydrolysis of ATP is –8 kcal/mol, and Δ G0 for the formation of the dipeptide is +0.5 kcal/mol. a. What is the net Δ G0 for this reaction? ___________________________ b. For a reaction at equilibrium, show the equation that relates Δ G0 to Keq. ______________________________________________________ c. In the following reaction, circle all the chemicals that bind to the enzyme’s active site. (Note: penalty for incorrect circles) Fructose 6—PO4 + ATP Fructose 1, 6—biphosphate + ADP d. What effect does increasing the enzyme concentration have on Keq? ____________________ e. If Keq>1, is the reaction endergonic or exergonic? _______________________________ 4. Having finished his Bio 1 lecture, Dr. Green is running to Rock Bottom when suddenly his muscles run out of oxygen. (a)_____________________________ starts getting reduced to lactic acid and the coenzyme (b) _____________________________________________ (do not abbreviate) gets oxidized so that glycolysis can continue. The coenzyme in (b) is derived from the vitamin (c)______________________. Halfway there, he catches his second wind and oxygen is resupplied to his muscles. Now pyruvate gets oxidized to (d)_________________________________ using the enzyme called pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The substance from (d) enters the Krebs cycle and (e)_________ mole(s) of ATP are produced per mole of pyruvate from the high energy substrate (f)___________________________. NADH and FADH2 are produced by the Krebs cycle and enter the electron transport chain to generate (g) __________ mole(s) of ATP per mole of FADH2 and (h)__________ mole(s) of ATP per mole of NADH. When glucose is completely oxidized by this process called (i) __________________________________, the total net moles of ATP produced per mole of glucose is (j) _________, and Dr. Green makes it to Rock Bottom just in time for Happy Hour. 5. Which type of transport applies to the following descriptions? (More than one answer may apply. Each answer may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Credit only for totally correct answers.) a) active transport b)passive transport c) facilitated diffusion d) endocytosis i. ii. iii. iv. Uses ATP ______________ Requires a protein _______________ Net transport from high to low concentrations _______________ Forms vesicles __________________ 6. a. Cells regulate their level of ATP primarily using an allosteric enzyme called ___________________________________________ (do not abbreviate if possible). b. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by lowering the ________________________________, thus speeding up the rate of reaction. c. What effect would the addition of mild acid (pH 5) to isolated mitochondria be expected to have on the rate of ATP synthesis by these organelles? Circle the correct answer. Hint: The acid accumulates in the intermembrane space. (a) Increase (b) Decrease (c) No effect Briefly explain your answer (1 sentence). d. The iron containing proteins called ____________________________ in the cristae of mitochondria creates a _____________________ gradient in the intermembrane space. 7. The secret of life according to Dr. Green is the ability to drive chemical reactions that are called (a)____________________________ reactions, such as the synthesis of (b)____________________________ from (c)__________________________, thereby creating order out of chaos. 8. Name 2 stages of meiosis at which genetic diversity occurs, and state what happens to produce this diversity. Stage Event a. b. c. At what stage of meiosis does the chromatin condense into chromosomes? ______________________________ d. What is a genetic process, other than mutations, by which genetic diversity occurs in bacteria? _______________________________________ 9. Bill and Monica are both heterozygous for two unlinked dominant traits: 1. Rapacious appetite (R), and 2. Lustful behavior (L). a. What are the genotypes of all the gametes Bill can produce? _______________________________ b. What fraction of this couple’s progeny would be predicted to have a rapacious appetite? ______________________ c. What fraction of their progeny would be predicted to be boys with a rapacious appetite? ______________________ d. What fraction of their progeny would be predicted to have both recessive traits? ______________________ 10. a. One exception to Mendel’s laws is seen when the heterozygote expresses a different phenotype than the dominant phenotype. This is known as __________________________________________________. b. When red homozygous dominant snapdragons (RR) were crossed with white homozygous recessive snapdragons (rr), the result is all heterozygous pink snapdragons (Rr). Draw a Punnet square to diagram the self-cross of the F1 progeny. c. What percentage of the F2 progeny are expected to be red? _________________________ d. What percentage of the F2 progeny are expected to be pink? ________________________ e. What percentage of the F2 progeny are expected to be white? _______________________ 11. a. b. c. d. Label the ends of each parental strand. Using arrows, show the direction of each newly replicating strand. Label the ends of each newly replicating strand. Indicate which newly replicating strand is being synthesized continuously by placing a C next to the correct strand. e. Name the enzyme that joins the discontinous DNA fragments _____________________________ 12. List the three major characteristics of the Genetic Code that were discussed in class. a. ___________________________________ b. ___________________________________ c. ___________________________________ d. A specific protein is composed of 30 amino acids. How many bases, including the start and stop signals, are necessary for the DNA to code for protein. ________________________ 13. Diagram a meiotic nondisjunction in which one X and one Y chromosome end up in the same gamete. Note: The dots represent centromeres holding the sister chromatids together. b. Most aneuploid embryos abort spontaneously because the cells synthesize either ______________________________ or _______________________________ protein. 14. a. It is difficult to prevent cancer because cancer is caused by _________________________, which may result randomly from radiation, chemical, and viruses. b. Every time a normal cell divides, the __________________________ shorten, but this does not happen in cancer cells, which is why they are thought to be “immortal”. c. p53 is an example of a gene called __________________________________, which helps prevent cancer because it induces a damaged cell to commit suicide, a process known as (d)______________________________________. e. Caffeine is a base analog that may cause cancer because it is definitely a ____________________________________ that inhibits DNA repair. 15. The lac operon is regulated both positively and negatively. Negative regulation occurs when an inducer called (a) ______________________________ binds to the (b)_______________________________ protein, causing it to dissociate from the operator so that (c)___________________________________ can now do its job by transcribing the DNA into mRNA. Positive regulation occurs when cyclic AMP binds to (d)_____________________________ forming a complex that binds to the promoter, making it strong, thus stimulating transcription of the lac operon. However, this only happens in the absence of (e)_______________________________. 16. a. Name the second messenger used together with adrenaline in the “fight or flight” response. _____________________________________ b. This second messenger activates an enzyme called ____________________________________. c. The enzyme in part b. facilitates post-translational control by adding a phosphate group from _________________________ to another enzyme, thereby activating or inactivating it. d. Steroid hormones regulate gene expression at the level of _______________________________. e. List the 2 other types of receptors found in the plasma membrane used for cell signaling. 1. G protein linked receptors 2. _________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________ 17. Name 3 roles that base-pairing has other than for the DNA double helix. a. _______________________________________ b. _______________________________________ c. _______________________________________ d. What does tRNA transfer from the cytoplasm to the ribosome? __________________________ e. How many tRNA’s are bound to a ribosome during the formation of one peptide? ______________________________ 18. a. Which of the three regions of the antibody (V, J, C) contains the specificity needed to recognize foreign antigens? __________________________________ (Do not abbreviate) b. After years of taking his TA’s to Rock Bottom for happy hour, Dr. G requires a liver transplant. Upon receiving a liver from a cadaver, Dr. G’s body rejects the new organ. Which of the 2 types of immunity is responsible for the rejection of the organ transplant? ___________________________ c. Which type of lymphocytes is used in the response in (b)? _______________________________ d. If a developing embryo had the following genetic regions, calculate how many possible different antibodies it could produce. _______________________________ Heavy Chain Genetic Regions Light Chain Genetic Regions V 100 100 J 5 4 C 2 1 e. The “clonal selection” theory proposes that a foreign antigen acts as a ____________________ (one word) when it binds to a specific lymphocyte, thereby generating a clone. 19. a. What is the function of a domain present in both RNA polymerase and protein kinase? ___________________________________ b. The DNA sequence of the above domain is very similar in E.coli and humans, with 16 out of 20 bases identical. What is the probability that this similarity occurs only by chance? P=_______________________________ (Don’t bother calculating the precise answer) c, d. What are 2 properties of mitochondria and chloroplasts that suggest these organelles were once free-living bacteria? 1. ________________________________ 2. ________________________________ 20. a. According to the readings, _________________ is the sex-determining gene located on the Y chromosome. b. According to the New York Times, it is widely agreed that the number of genes to the human genome is approximately _________________________. c. The gene _______________ has the ability to stop tumors before they grow, but if damaged, this gene is involved in 60% of cancers. d. White males with the mutation located in the gene ____________________ have been found to be HIV resistant. e. The letters in PCR stands for ________________________________________________. BONUS (4 points) What is Dr. G’s favorite organism? What good is a buffer if it cannot bark?