* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mountain Glacier Melt to Contribute 12 Centimeters to World Sea
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
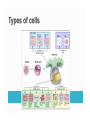
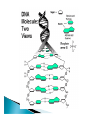
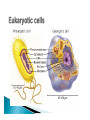
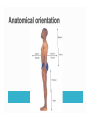
Mountain Glacier Melt to Contribute 12 Centimeters to World Sea-Level Increases by 2100 ScienceDaily (Jan. 11, 2011) — Melt off from small mountain glaciers and ice caps will contribute about 12 centimetres to world sea-level increases by 2100, according to UBC research published this week in Nature Geoscience. Capacity for metabolism Responds to environment Capable of reproduction Basic structure 1. Plasma membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. DNA 4. Ribosomes Lipid bilayer – hydrophobic “Wall with doors” Channels, pumps, receptors Semifluid goo Everything inside plasma membrane that is not the nucleus or organelles Water, salts, proteins Deoxy ribo Nucleic Acid Set of instructions for cell’s function & development Sugar & phosphate backbone Nucleotide base pairs = “rungs” ◦ Adenine ◦ Thymine ◦ Guanine ◦ Cytosine Proteins 3D structure Binding sites, active sites, structure DNA -> RNA -> amino acid chains -> folding > proteins DNA RNA Amino Acid Protein GCT (codon) GCU (Thymine -> Uracil) Alanine ********Alanine**Stop Lysozyme CHONSP Carbon – every molecule Hydrogen – same Oxygen – photosynthesis & respiration ◦ Make ATP Nitrogen – proteins Sulfur – proteins Phosphorus - DNA Adenosine Tri-Phosphate ATP ADP release energy Mitochondria: ◦ ADP + energy = ATP Making proteins Transporting molecules across plasma membrane Muscle contraction More CO2 + H2O + light energy glucose + O2 Most organisms Sugars + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy ADP + energy ATP Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Midsagittal plane Frontal / Coronal plane Transverse plane