* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle Check
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
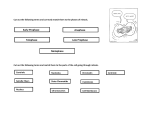
Cell Cycle Check 1. Draw the cell cycle as a pie graph. Include: mitosis, interphase, G1, S, G2. 2. Next to each label above, write 1-4 words about the function. Mitosis Check 1. Define mitosis and tell why it is important. 2. Differentiate between mitosis and cytokinesis. 3. Why do chromosomes form chromatin? 4. What is the purpose of the S phase of the cell cycle? 5. In what phase of the cell cycle does replication occur? Why is it important? 6. How is binary fission different from mitosis? 7. What is a plasmid? Why is it important? 8. What is the role of a spindle fiber? A centriole? 9. What is a meristmatic region? Where can you fine one? 10. Compare and contrast DNA in a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. True/False 1. Asters form from centrioles 2. Plants form cleavage furrows. 3. Centrioles can replicate. 4. Chromosomes are joined by chromatin. 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophase. 9. DNA strands in eukaryotic cells exist in multiples of two. 10. The “poles” are creaked by the spindle fibers. 11. Two pairs of chromatids attach to each spindle fibers. 12. DNA is not visible in interphase 13. The G2 phase helps a cell get ready for mitosis. 14. Cells stuck at G0 do not divide. 15. Bacteria are all clones of each other (no recombination). 16. If a skin cell does mitosis it produces clones of itself. 17. The major purpose of metaphase is to separate chromatids. 18. Humans have 92 strands of DNA in metaphase