* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO STUDY GUIDE - Biochemistry and Cells
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
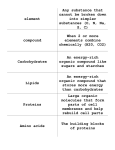
Biochemistry and Cells Review Guide This is one of the largest and most in-depth units that you’ll be assessed on – DON’T WAIT UNTIL THE LAST NIGHT TO STUDY FOR THIS EXAM!! Exam: Feb. 26th Biochemistry 1. Which of the four main types of organic molecules are polymers? 2. What does the term organic mean? 3. What is the valence number of electrons for Carbon? 4. Proteins are made of what? 5. Enzymes fall into which of the four main classes of organic molecules? 6. Bases have what pH? Acids have what pH? 7. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat? 8. From your notes/lab, what are some examples of acids and bases? 9. What particles are in an atom? 10. Water molecules are polar. What does this mean? 11. What are the basis building blocks of starch? 12. Which of the four main classes of organic molecules serves as the main source of energy for living things? 13. What functions do proteins serve? 14. What happens to atoms during a chemical reaction? 15. What is a reactant and a product? 16. Define activation energy. 17. In what form can energy be released during a chemical reaction? 18. What are enzymes and under what conditions do they work best? 19. What is a catalyst? 20. What smaller particles make up nucleic acids? 21. How is the name of an enzyme distinguished? 22. What are adhesion and cohesion? 23. Name the four main types of organic molecules. 24. What do enzymes do in cells? 25. What do the terms solution, solute and solvent mean? 26. Vocabulary: a. Polymer b. Monomer c. Polypeptide d. Nucleotide e. Enzyme f. Polar Molecule g. Organic h. Monosaccharide – formula i. Disaccharide – formula j. Polysaccharide – formula k. Denaturation l. Ester bon m. Peptide bond n. Glycocidic bond o. Dehydration synthesis p. Hydrolysis q. Ionic bon r. Covalent bond s. Polar covalent bond t. Ion u. Isomer v. Isotope w. Hydronium ion x. Hydroxide ion y. Diffusion z. Osmosis aa. Glycogen bb. Plant starch cc. Hemoglobin dd. glucose 27. What types of things could alter the function of a protein molecule? 28. Review the chemistry quiz … you may see these types of questions again! (know how to use the periodic table). 29. balance equations (simple … matter can not be created or destroyed but it may be rearranged). 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What tests are used to identify the following: -monosaccharides -polysaccharide – plant starch - proteins – turn yellow -proteins – turn purple -fats 33. Which organic compound provides energy quickly? 34. Which organic compound is digested the fastest? 35. Where is glycogen stored? 36. Hemoglobin, an organic transport protein, is present in what type of cell? 37. Lipids: cell membrane / nonpolar / insoluble 38. Review the parts of the scientific method. a. What is a control and what is its purpose? Cells 1) Understand the following words: a) organelles b) prokaryotic cell c) cytosol d) nucleoid e) chromatin f) vesicles g) transport vesicle h) phagocytosis i) food vacuoles j) mitochondrial matrix k) plastids l) thylakoids m) granum n) stroma o) cytoskeleton p) microtubules q) microfilaments r) intermediate filaments s) centrosome 2) Be able to label the organelles on plant and animal cell diagrams. 3) State the structure/function relationship for the following: a) plasma membrane b) cell wall c) cytoplasm d) nucleus e) nucleolus f) ribosomes g) rough endoplasmic reticulum h) smooth endoplasmic reticulum i) Golgi Apparatus j) k) l) m) n) o) p) q) r) mitochondria lysosomes peroxisomes vacuole chloroplasts chromosomes centrioles cilia flagella 4. Be able to label the parts of a plasma membrane diagram. 5. Study the following information in your class notes: s) the components of the plasma membrane t) characteristics of the plasma membrane u) types of proteins in the plasma membrane v) functions of proteins in the plasma membrane w) definition of homeostasis x) definition of selectively permeable y) definition of passive transport z) information on diffusion – concentration gradient, and selectively permeable aa) definition of osmosis bb) three different conditions for osmoregulation – hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic cc) description of facilitated diffusion dd) description of active transport ee) definition of endo- and exocytosis Cell Energy Overarching Concept: Energy production through chemiosmosis 3. Cellular Respiration a. aerobic respiration b. glycolysis a. cytoplasm c. produce 2 ATP & 2 NADH d. substrate-level phosphorylation Krebs cycle a. mitochondrial matrix c. produce electron carriers (NADH & FADH2) + 2 ATP + CO2 (waste product) ETC a. mitochondrial inner membrane: cristae increase surface area b. protein pumps embedded in membrane: cytochromes c. establish H+ gradient in intermembrane space, so they flow into matrix through ATP synthase d. produce ~40 ATP e. oxidative phosphorylation i. O2 = final electron acceptor b. anaerobic respiration: glycolysis, fermentation low ATP production (~2 ATP) alcohol fermentation lactic acid fermentation Cell division a. Cell cycle interphase; mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase; cytokinesis G0, G1, S, G2 b. Produces genetically identical clones c. Replication DNA polymerase (I & III), leading strand, lagging strand, helicase, single-stranded binding proteins, ligase, primase, RNA primer, Okazaki fragments, telomeres d. Regulation G1/S & G2/M checkpoints, cdKs, cyclins, growth factors cancers are caused by loss of cell cycle control