* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ALS - AJNR Blog
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Tuberous sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
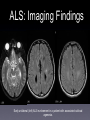
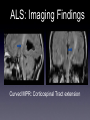
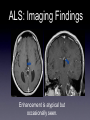
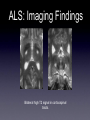
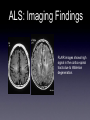
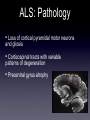
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Ali Nasim MD Fellow, Neuroradiology Division at UNC What is ALS? •A-myo-trophic = no-muscle-nourishment •Lateral Sclerosis refers to involvement of the lateral corticospinal tracts. •ALS is a degeneration of somatic motor neurons extending from upper motor cortical pyramidal neurons to lower motor neurons of the brainstem and cord. History of ALS • 1869 - First described in publication by Dr. Jean-Martin Charcot, in Paris. • 1881 - Lectures translated into English ALS: Clinical Findings Symptoms: •Upper motor - Babinski, spasticity, hyperreflexia. •Lower motor - asymmetric muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculations •Bulbar signs - dysphagia, slurred speech ALS: Clinical Findings Types: •Classic - UMN and LMN •Only UMN or only LMN •Predominantly bulbar form - worse prognosis •Familial - 15-20% • 5600 cases per year in the US, 40-70 y/o, M:F 2:1 ALS: Clinical Findings • Progresses distal to proximal, with complete disability within 10 yrs • 20% of patients survive >5 yrs •Familial and juvenile onset survive 20-30 yrs after diagnosis ALS: Clinical Findings • Revised El Escorial World Federation of Neurology criteria: • Evidence of LMN degeneration by clinical, electrophysiological, or neuropathological examination • Evidence of UMN degeneration by clinical examination • Progressive spread of symptoms or signs within a region or to other regions (The body is divided into four regions: cranial, cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral) • Absence of electrophysiological, pathological or neuroimaging evidence of other disease processes. ALS: Imaging Findings •Can have normal imaging •Focal atrophy in chronic cases • T2/FLAIR hyperintensity extending along the corticospinal tract from corona radiata to the brainstem • Contrast enhancement - ? •Deposition of iron in affected cortex ALS: Imaging Findings Early unilateral (left) ALS involvement in a patient with associated callosal agenesis. ALS: Imaging Findings Curved MPR: Corticospinal Tract extension ALS: Imaging Findings Enhancement is atypical but occasionally seen. ALS: Imaging Findings Bilateral high T2 signal in corticospinal tracts. ALS: Imaging Findings Increased iron (low T2 signal) deposition in the gray matter of the peri-Rolandic regions which underlying high signal in the white matte and dilatation of the adjacent cortical sulci. ALS: Imaging Findings FLAIR images shows high signal in the cortico-spinal tracts due to Wallerian degeneration. ALS: Imaging Findings •MR Spectroscopy: • Decreased NAA/Cr ratio • Increased choline and myoinositol • Decreased glutamate in the precentral gyrus and peri-rolandi white matter ALS: Pathology • Loss of cortical pyramidal motor neurons and gliosis • Corticospinal tracts with variable patterns of degeneration • Precentral gyrus atrophy ALS: Pathophyiology • Cause of Spontaneous ALS unknown • Single gene mutations can lead to selective motor neuron loss • Glutamate excitotoxicity (etiology unknown) ALS: Pathophyiology Familial ALS: • Copper/Zinc Superoxide dismutase (SOD1)gene mutation found to be associated with 20% of familial ALS • Gain of function mutation ALS: Interesting Info • Reports of populations with increased incidence, most notably the Chamarro people of Guam (ALS-PCD) • Incidence ranging 140-400 cases / 100,000 (nml 0.5-2 cases/ 100,00) • Recent theory is that this was due to bat consumption and exposure to BMMA excitotoxins. ALS: Notable People Affected Lou Gehrig Stone Stephen Hawking Jon ALS: Treatment •Riluzole - glutamate release inhibitor -Has been shown to increase NAA/Cr ratio •Symptom treatment - ventilation, anti-spastic medications References • Kalra, S. et al, Neuroimaging in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. ALS and Other Motor Neuron Disorders. 2003:4 243-248. • Kalra, S. et al, Gabapentin Therapy for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Lack of Improvement in Neuronal Integrity Shown by MR Spectroscopy AJNR, Mar 2003; 24: 476 - 480. • Bowen, B. , MR Imaging and Localized Proton Spectroscopy of the Precentral Gyrus in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis AJNR, Apr 2000; 21: 647 - 658. • statDx.com • archives.org • athiestnexus.org • sabine.k12.la.us • muppet.wikia.com