* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - Cobb Learning
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
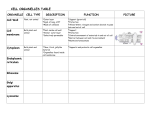
Cells: Microscopes, Cell Structure, Function, and Organelles Study Guide You need to answer the following questions or define the word on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three parts of the cell theory? Make sure you know all of them! 2. What is the outer boundary of the cell called? 3. What are organelles that use energy from sunlight to produce food called? 4. Are plant and animal cells larger or smaller than bacterial cells? 5. What is the source of energy for most autotrophs? 6. What is the function of the cell wall? 7. What is the function of the cell membrane? 8. What organelle produces almost all of the energy a cell needs? 9. What organelle produces proteins from amino acids in the cell? 10. What organelles release chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones? 11. How does a plant or animal cell differ from a bacterial cell? 12. What organelles that are found in plant and animal cells are also found in bacteria cells?? 13. The cells in many-celled organisms look the same, have the same structure, or are quite different from one another?…..pick one! 14. What is an organism called that is composed of many cells? 15. What structure allows materials to pass into and out of a cell? 16. What are the thin strands inside the nucleus that contain genetic material called? 17. What do chloroplasts do and which types of cells have them? 18. What is cytoplasm? 19. What does the Golgi complex do? 20. What do lysosomes do? 21. Recognize the formul for photosynthesis! 22. Cellulose is found in what type of cells? 23. Where is the genetic material found in a plant and animal cell? 24. Where is the genetic material found in a bacteria cell? 25. What does the genetic material in DNA do? 26. What structure is found in plant and bacterial cells but not in animal cells? 27. The energy that cells create is called what? 28. Why are cells so small? What can happen if a cell’s volume grows faster than its surface area? 29. Make a Venn Diagram or a chart, comparing a plant and animal cell and also create one comparing a Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell. 30. List these in correct order from smallest to largest: Tissue, Organism, Cells, Organ system, Organ 31. Make sure you have studied the picture of a plant, animal and bacterial cell and you are familiar with what the organelles look like. 32. All organisms share what characteristics (6)? 33. Give 3 examples of stimuli and their responses. 34. What is homeostasis and why is it important? 35. What % of the body is water? 36. What are used by cells for energy storage? 37. What are proteins and what are they used for? 38. All living things are made up of what? 39. What are the 4 necessities (basic needs) of living things? 40. What does shivering do when our bodies are faced with cold as a stimulus? 41. The function of a cell is related to its ____________ 42. What is formed of thousands of nucleotides? 43. What is the process for plants to change sunlight into sugar? 44. Every cell membrane is made up of what kind of molecules? 45. What is in the content of the fluid surrounding a cell? 46. What are the 5 building blocks of cells and what life functions do they perform? 47. What molecules form most of the bilayer cell membrane? 48. Which molecule provides energy for cell processes? Where is it made?