* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Humble ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
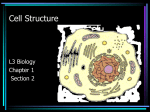
Name _____________________________________________________________ Test Date _Block Day, 9/15 or 9/16___ UNIT II – INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell/ I. TYPES OF CELLS (p.172, 173) All living things are made of _cells____ and all cells can be divided into two groups A. Prokaryotic – “_Before nucleus__” Prokaryotic cells lack a true _nucleus___ and other _membrane__- bound internal structures. Prokaryotic cells do contain _DNA_____, usually concentrated in a particular region of the cell. All prokaryotes are _bacteria___ and all _bacteria are prokaryotes____. B. Eukaryotic – “_True___ _nucleus___” Eukaryotic cells contain a _nucleus_______ and other membrane-bound structures. Eukaryotic organisms may be _unicellular (single-celled)_____ or _multicellular____. In multicellular organisms, cells become _specialized______. II. DISCOVERY OF CELLS (pp.169-172) A. History of Microscopes The invention and development of the microscope in the 1600s enabled scientists to discover and study cells. 1. Anton van Leeuwenhoek - Was the first to try stacking several _lenses____ together to view tiny objects. He looked at _pond water________ through his lenses and became known as the first scientist to describe living cells as seen through a microscope. 2. Robert Hooke - Used a microscope to examine thin slices of cork. He called the tiny boxes he saw _cells_________. He chose the name "cells" because the chambers he saw reminded him of the small rooms in a _monastery_______, which were called cells. B. Cell Theory The discoveries and observations of scientists such as _Schleiden____, _Schwann_______, and _Virchow___ led to the development of the _Cell Theory____________ in the mid 1800s. The Cell Theory states that: 1. All _living things _ are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the _smallest working unit of life_______. 3. All cells come from _other cells___ through _cell division____. C. Modern Microscopes There are several types of modern microscopes: 1. Compound light microscope – Contain more than one _lens___ and uses _light rays____ bent through _glass__ to magnify objects. Type of microscope used in the classroom. 2. Electron microscope – Uses a beam of _electrons_____. Specimen must be kept in a _vacuum_____. Offers the advantage of much greater _magnification____ but specimen must be _non-living_______. There are 2 types of electron microscopes: a. scanning electron microscope or _SEM__________ - traces the _surface________ of the specimen and forms a 3D image b. transmission electron microscope or _TEM_________ - aims electron beam through specimen. Used to examine _internal___ cell structures. III. CELL BOUNDARIES (pp.182-183) A. Cell Wall Cell walls are the outermost boundary in _plants____, _fungi________, and _bacteria___________. They are not found in _animal cells________________. The primary function of the cell wall is to provide _structure and support________. The cell wall does not regulate what _enters and leaves___________ the cell. 1. Cell walls of plants are composed of _cellulose_________________ 2. Cell walls of fungi are composed of _chitin____________________ B. Cell Membrane Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane made of ___________________. The cell membrane is selectively permeable which means _it only allows certain substances in and certain substances out________. This characteristic is critical in helping the cell maintain _homeostasis____. The cell membrane is also called the _plasma_____ membrane. IV. INSIDE A EUKARYOTIC CELL (pp. 174-181) The inside of the cell consists of the: A. Nucleus B. Cytoplasm – Includes the _cytosol__________ or “cell gel” and the _organelles________, which means “_little organs____” V. EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURES Illustration Structure Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope Ribosomes Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Plant Animal Characteristics & Function _Control center___ of the cell. Genetic information stored as _chromatin______, which is _DNA________ wrapped in _protein____. Small, dense region in the nucleus. Site of _ribosome____ production. Double _phospholipid______ membrane. Has nuclear _pores_____ which allow _RNA______ to leave the nucleus Tiny, granular organelles located on _endoplasmic reticulum_____ or suspended in _cytosol_______. Site of _protein production_____. All cells (pro & euk) have ribosomes. Extensive network continuous with _nuclear envelope_____. Called “rough” because it has _ribosomes___ all along the membrane. Function of the rough ER is to _modify & transport proteins_____. Most of these proteins are packaged into _vesicles______ (like bubbles or sacs) and shuttled to the __Golgi apparatus________ Similar to rough ER in structure, except that it lacks _ribosomes__. The smooth ER manufactures _lipids____, breaks down _glycogen___, detoxifies _poisons__, and _stores calcium_____. Golgi apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Mitochondria Found in _animal__ cells only. Round sacs containing _enzymes___ that _break down___ and _recycle_____ used cell components. Also used as defense against _bacteria_____ and _viruses__ Sacs that may be used as storage for _water___, _molecules__, _molecules__, or wastes. Plants have a large central vacuole. Double-walled organelle with inner folds _to increase surface area____. Uses _glucose_____ to manufacture energy in the form of _ATP____. Mitochondria have their own _DNA____. Chloroplast Found in _plant____ cells. Contain _chlorophyll_____ (green pigment) and their own _DNA______. Chloroplasts harvest energy from the _sun___ to produce _ATP___ through _photosynthesis___. Centrioles Found in _animal____ cells only. Bundles of _microtubules_______ that play a role in _cell division_____ Cytoskeleton VI. THE PROKARYOTIC CELL Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack of _pancakes_____. Receives, modifies, and ships products by way of _vesicles____ into the _cytosol → cell membrane_______ Composed of protein fibers known as _microtubules____ and _microfilaments_______. Anchor _organelles_____ and provide _structure_____. Also provide motility for some cells in the form of _cilia___ or _flagella____. More extensive cytoskeleton found in _animal___ cells. VII. THE EUKARYOTIC CELL