* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download # Unit 4 LT1
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
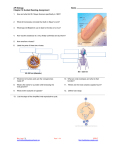
# Unit 4 LT1 Use the diagram to help you to explain why surface area-to-volume (s.a./vol) ratios are important to a dividing cell. # When cells divide, their surface area (supply of nutrients across the plasma membrane) decreases slower, by length2 while volume (metabolic demand) decreases faster by length3. Mitotic cell division gives the cell a much more favorable surface area to volume ratio. Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 1 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com # Unit 4 LT1 Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? The model presented in class used two large rubber bands twisted together to represent the circular DNA of a prokaryotic cell. They adhere to the plasma membrane at the equator of the plasma membrane. As cytokinesis occurs, the two rings of DNA are pulled apart into their half of the cell. Two cells are formed this way. It is called binary fission. (“2” – “separating”) They are genetically identical (except for the plasmid DNA that was divided by chance). Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 2 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com # Unit 4 LT2a Identify the phases of the cell cycle. the long, round arrow the short, split arrow each of the five pie wedges the name for the resulting cells Please do not mark on this paper. # daughter cells Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 3 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com # Unit 4 LT2c Put the following descriptions of each the events of each of the phases in the proper chronological order. Cytoplasm is divided by the “purse-string mechanism” in animal cells and by creating a cell plate in plant cells. 1. Chromosomes are single-stranded. Mitochondria divide Cell grows: adds membrane for larger membrane-bound organelles. Supply of monomers and ATP increase. Includes a checkpoint for readiness. 2. DNA is replicated Protein production and metabolism on “hold.” 3. Chromosomes are double-stranded. Mitochondria divide Cell grows: adds membrane for larger membrane-bound organelles. Supply of monomers and ATP increase. Includes a checkpoint for readiness. 4. Nuclear information is arranged and divided 5. Cytoplasm is divided by the “purse-string mechanism” in animals and by creating a cell plate in plant cells. Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 4 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com Unit 4 LT2d Cancer is considered a disease of the cell cycle. Explain why. Cancer cells divide out of control. They are not governed by the chemical messages that control the cell cycle. Sometimes, mutations cause the loss of expression of the p53 or guardian angel gene/protein which protects the individual by destroying cancerous cells. If this is then followed by a mutation for over-expression of the “divide” command (the Ras gene/protein), the cell becomes cancerous and divides until a tumor forms. Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 5 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com Unit 4 LT3 Use your knowledge of mitotic events to identify and label each phase of mitosis. This cell is in the cell cycle phase called interphase; it is not in mitosis. Prophase: Chromosomes are distinct but nuclear envelope and nucleolus are still visible. of Metaphase: Chromosomes form a single file line at the metaphase plate through the equator the cell. “Chromosomes met at metaphase” Anaphase: Chromosomes have moved to opposite poles but no cell plate is yet visible. Notice the spindle fibers. Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 6 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com Name the parts of the chromosome. Use this word bank: Mrs. Loyd [email protected] Page 7 of 7 1/29/15 http://loydbiology.weebly.com