* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3/Final Exam Study Guide
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
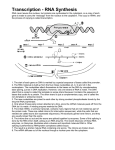
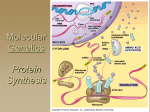
Exam 3 Study Guide Thursday, August 16th 10:50am-1:00pm 6 short answer questions – 50 points No complete sentences required Variable points (denoted next to the question) You may draw structures and pictures as needed 1 short essay – 40 points All possible questions given below 44 multiple choice questions 2.5 points each Plus bonus questions! Lecture Breakdown Multiple choice and short answer questions from previous exams – 30% Of the remaining questions… o Lecture 15 – 20% o Lecture 16 – 25% o Lecture 17 – 15% o Lecture 18 – 5% o Lecture 19 – 15% o Lecture 20 – 20% Example questions 1. Briefly describe the race to complete the human genome. Include descriptions of the government-funded group, the privately-funded group, the people involved, and the differences in the sequencing techniques. Recommended viewing. 2. In 1987, Genentech was the first company to create a biologic through genetic engineering of E. coli. They inserted the human eukaryotic gene for insulin production into the prokaryote, which caused the bacteria to produce insulin. They then purified the insulin, packaged it, and sold it as a drug. However, in order to have the gene accurately expressed they had to do a couple modifications. What might those modifications have been like? Use the terms introns, exons, splicing, 5’ cap, and poly-A tail. 3. What are the four phases of clinical trials and their characteristics? 4. What is bt toxin? What is it used for, and how does it work? 5. You are treating a patient who has recently severed their spinal cord. What sort of treatment would be best to give them to improve their long-term quality of life? a. Morphine or other opiods to eliminate pain b. Gene therapy to trigger genes that control cell division in neural cells c. A monoclonal antibody regimen that would target and destroy the damaged neural cells d. An injection of human neural stem cells to regrow damaged neural cells 6. Which of these is NOT a trait we would genetically engineer into plants? a. Herbicide resistance b. Production of pesticides c. Increased taste or nutrition d. Crop yield e. Carcinogenicity 7. Which of the following is NOT an advantage for induced pluripotent stem cells? a. They are probably not immunogenic to their host b. They may not be equivalent to embryonic stem cells c. There are few political and ethical objections to their use in research d. They were created using retroviral transformation and therefore contain retroviral elements in their genome Possible short essay questions 1. How does a cell transcribe information from DNA to RNA in eukaryotes? Use the following terms: RNA polymerase Transcription Introns, exons Initiation, elongation, termination RNA splicing Promoter preMRNA TATA box 5’ cap, Poly-A tail Transcription factors 2. How does a cell translate information from RNA to protein in eukaryotes? Use the following terms: Stop and start signals Codon Release factor Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase Initiation, elongation, termination Ribosome Methionine Small subunit, large subunit tRNA EPA Anticodon 3. Draw or explain the process of DNA replication. Include the following terms: Helicase Leading strand DNA polymerase Lagging strand RNA primase Initiation, elongation, termination DNA Ligase Origin of replication Okazaki fragment BIOL 211 Spring 2012 Vocabulary • • • • • • • • • • • Central dogma of molecular biology Helicase DNA polymerase RNA primase Topoisomerase DNA ligase Origin of replication Initiation, elongation, termination Mismatch repair Nucleotide Excision repair Mechanism of telomere shortening • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • RNA world Ribozyme Out of Africa hypothesis Mitochondrial Eve Haplogroup, haplotype Craig Venter, Francis Collins NIH, Celera, Human Genome Project One gene, one protein hypothesis Exons, introns Alternative splicing HERVs Pseudogenes LINEs, SINEs Transposons, retrotransposons ALU elements Microsatellites Carcinogen Mutagen Point mutation Silent mutation Missense mutation Nonsense mutation Frameshift mutation Indel • • • • • • • • • • • • Post-translational modification Glycosylation Chaperonins Antibiotics Polyribosomes Stop signals Release factor Translation Initiation, elongation, termination Methionine tRNA Anticodon • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase Ribosome Small subunit, large subunit EPA Spliceosomes Alternative splicing Introns, exons RNA splicing preMRNA 5’ cap, Poly-A tail Transcription Initiation, elongation, termination Promoter Enhancer TATA box -10 and -35 sequences Transcription factors Sigma factor RNA polymerase Degenerate code Codon Template strand • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Small-molecule, biologic Embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, iPSCs Totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent Antibodies Gene therapy Publish or perish Preclinical development Clinical Trials phases I-IV In vivo, in vitro, in silico FDA Valley of death Blockbuster drugs “Me too” drugs Drug development pipeline Embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, iPSCs – Totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent Gene therapy Vector Immunogenesis, tumorigenesis bt toxin Ti plasmid Biolistics Roundup Biofuels • • • • • • • • BIOL 211 Spring 2012 • • • 1st generation, 2nd generation, 3rd generation biofuels Ethanol biofuels Biodiesel • • • Cloning DNA cloning, therapeutic cloning, reproductive cloning Dolly the sheep