* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operant Conditioning
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Flagellation wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Negative affectivity wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
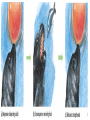
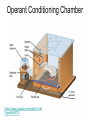
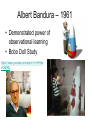
DO NOW Pre-assessment 1. What is another word that means the same thing as negative reinforcement? 2. When negative reinforcement is supplied, it usually results in: a. Weakening a behavior that you want weakened. b. Strengthening a behavior that you want strengthened. 3. Do people usually look forward to negative reinforcement? a. Yes b. No 4. Will you regularly (consciously) use positive reinforcement in the future? a. Yes b. No 5. Will you regularly (consciously) use negative reinforcement in the future? a. Yes b. No Lesson 6.3 Operant Conditioning • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. REINFORCEMENT PUNISHMENT OPERANT CONDITIONING REINFORCEMENT (increase behavior) PUNISHMENT (decrease behavior) POSITIVE (adding something to the situation) NEGATIVE (removing something from the situation) (+) (-) POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT POSITIVE PUNISHMENT NEGATIVE PUNISHMENT Reinforcer • Any event that STRENGTHENS the behavior it follows. Two Types of Reinforcement: Positive and Negative Positive Reinforcement • STRENGTHENS a behavior by ADDING a stimulus after a response • INCREASING the behavior of doing chores by ADDING money Positive Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement • STRENGTHENS a behavior by REMOVING an aversive stimulus. • INCREASING the behavior of smoking by REMOVING the anxiety Negative Reinforcement Punishment • An event that DECREASES the behavior that it follows. Positive Punishment • DECREASES a behavior by ADDING a stimulus after a response. • DECREASING the behavior of misbehaving by ADDING a spanking Negative Punishment • DECREASES a behavior by REMOVING an aversive stimulus. • DECREASING the behavior of texting by REMOVING the cell phone Limitations of Punishment • Punishment often only produces temporary suppression • Punishment produces undesirable emotional side effects • Children who are physically punished learn to model or imitate aggressive acts and often become more aggressive in their interactions with others • Punishment NEVER teaches a new behavior Making Punishment more Effective • Apply punishment immediately • Apply punishment consistently • Apply punishment moderately • Avoid withholding love • Countercondition (reinforce alternative positive behaviors) DO NOW – Classical or Operant? • A band begins its tour featuring many new, unreleased songs, all of which draw silence from the people at their concerts. The same people cheer wildly when the band plays any of its old hits. Gradually, the band reduces the number of new songs it plays and starts playing more of the old ones. (If classical, identify UCS/UCR/CS/CR) (If operant, indicate which type) YESTERDAY’S HW - ANSWERS 1. Positive Punishment 9. Negative Reinforcement 2. Positive Reinforcement 10. Positive Punishment 3. Negative Reinforcement 11. Positive Reinforcement 4. Positive Reinforcement 12. Positive Reinforcement\ 5. Negative Reinforcement 13. Positive Reinforcement 6. Positive Punishment 14. Negative Punishment 7. Negative Reinforcement 15. Positive Reinforcement 8. Positive Reinforcement 16. Positive Reinforcement OPERANT CONDITIONING REINFORCEMENT (increase behavior) PUNISHMENT (decrease behavior) POSITIVE (adding something to the situation) NEGATIVE (removing something from the situation) (+) (-) POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT POSITIVE PUNISHMENT NEGATIVE PUNISHMENT Operant Conditioning on Pigeons • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mDntb GRPeEU Edward Thorndike - 1905 • Law of Effect: behavior followed by favorable consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely • basis of Operant Conditioning Thorndike’s Cat Puzzle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BDujDOLre-8 B. F. Skinner - 1948 Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer Operant Conditioning Chamber https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M OgowRy2WC0 Observational Learning • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7d4gm dl3zNQ What is Observational Learning? Modeling: Learning by observing and imitating the behavior of others Albert Bandura – 1961 • Demonstrated power of observational learning • Bobo Doll Study https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hHHdo vKHDNU Observational Learning (Modeling) • Prosocial Behavior – positive, constructive, and helpful behavior • Antisocial Behavior – negative, destructive, and hurtful behavior