* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download This is Where You Type the Slide Title
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Political psychology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Administrative Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Vladimir J. Konečni wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
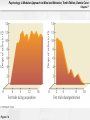
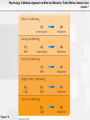
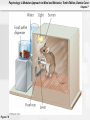
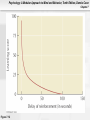
Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Chapter 7: Conditioning and Learning Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Learning: Some Key Terms • Learning: Relatively permanent change in • behavior due to experience – Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, injury, maturation, injury, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning Reinforcement: Any event that increases the probability that a response will recur Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Learning: Some More Key Terms • Response: Any identifiable behavior – Internal: Faster heartbeat – Observable: Eating, scratching Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Learning: Two More Key Terms • Antecedents: Events that precede a response • Consequences: Effects that follow a response Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Classical Conditioning • Ivan Pavlov: Russian physiologist who initially • • • was studying digestion Used dogs to study salivation when dogs were presented with meat powder Also known as Pavlovian or Respondent Conditioning Reflex: Automatic, nonlearned response Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.3 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Table 7.1 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Basics of Classical Conditioning Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Principles of Classical Conditioning • Acquisition: Training period when a response • • is strengthened Higher Order Conditioning: A conditioned stimulus is used to reinforce further learning Expectancy: Anticipation concerning future events or relationships Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 More Classical Conditioning Terms • Extinction: Weakening of a conditioned • response through removal of reinforcement Spontaneous Recovery: Reappearance of a learned response following apparent extinction Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.4 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.5 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 More Principles of Classical Conditioning • Stimulus Generalization: A tendency to • respond to stimuli that are similar, but not identical to, a conditioned stimulus (e.g., responding to a buzzer or a hammer banging when the conditioning stimulus was a bell) Stimulus Discrimination: The learned ability to respond differently to similar stimuli (e.g., Anya will respond differently to various bells: alarms, school, timer) Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Features and Phases of Classical Conditioning Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.6 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Classical Conditioning in Humans • Phobia: Intense, unrealistic, irrational fear of • a specific situation or object (e.g., arachnophobia, fear of spiders) Conditioned Emotional Response (CER): Learned emotional reaction to a previously neutral stimulus Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Classical Conditioning in Human (cont.) • Desensitization: Exposing phobic people • gradually to feared stimuli while they stay calm and relaxed Vicarious Classical Conditioning: Learning to respond emotionally to a stimulus by observing another’s emotional reactions Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.7 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Operant Conditioning (Instrumental Learning) • Learning based on the consequences of • responding; we associate responses with their consequences Law of Effect (Thorndike): The probability of a response is altered by the effect it has; responses that lead to desired effects are repeated; those that lead to undesired effects are not Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 More Operant Conditioning Terms • Operant Reinforcer: Any event that follows a • • response and increases its likelihood of recurring Conditioning Chamber (Skinner Box): Apparatus designed to study operant conditioning in animals Response-Contingent Reinforcement: Reinforcement given only when a particular response occurs Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Rat in a Skinner Box Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.8 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.9 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Timing of Reinforcement • Operant reinforcement most effective when • • given immediately after a correct response Effectiveness of reinforcement is inversely related to time elapsed after correct response occurs Response Chain: A linked series of actions that leads to reinforcement Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Timing of Reinforcement (cont.) • Superstitious Behavior: Behavior that is • • repeated to produce reinforcement, even though it is not necessary Shaping: Molding responses gradually in a step-by-step fashion to a desired pattern Successive Approximations: Ever-closer matches Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Operant Extinction • Definition: When learned responses that are • NOT reinforced gradually fade away Negative Attention Seeking: Using misbehavior to gain attention Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.10 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.12 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 More Operant Conditioning Terms • Positive Reinforcement: When a response is • followed by a reward or other positive event Negative Reinforcement: When a response is followed by the removal of an unpleasant event (e.g., the bells in Fannie’s car stop when she puts the seatbelt on); ends discomfort Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Punishment • Any event that follows a response and • decreases the likelihood of it recurring (e.g., a spanking) Response Cost: Reinforcer or positive thing is removed (e.g., losing Xbox™ privileges) Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.1 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Types of Reinforcers • Primary Reinforcer: Nonlearned and natural; • • satisfies physiological needs (e.g., food, water, sex) Intracranial Stimulation (ICS): Natural primary reinforcer; involves direct electrical activation of brain’s “pleasure centers” Secondary Reinforcer: Learned reinforcer (e.g., money, grades, approval, praise) Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 More Reinforcer Types • Token Reinforcer: Tangible secondary • reinforcer (e.g., money, gold stars, poker chips) Social Reinforcer: Provided by other people (e.g., learned desires for attention and approval) Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.14 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.16 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Feedback and Knowledge of Results • Information about the effect a response had • Knowledge of Results (KR): Increased feedback; informational Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Programmed Instruction • Information is presented in small amounts, • • gives immediate practice, and provides continuous feedback Computer-Assisted Instruction (CAI): Learning is aided by computer-presented information and exercises Educational Simulations: Explore imaginary situations or “microworld” that simulates realworld problems (e.g., “The Sims” computer simulation) Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.17 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.18 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Partial Reinforcement • Reinforcers do NOT follow every response • Schedules of Reinforcement: Plans for • • determining which responses will be reinforced Continuous Reinforcement: A reinforcer follows every correct response Partial Reinforcement Effect: Responses acquired with partial reinforcement are very resistant to extinction Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Schedules of Partial Reinforcement • Fixed Ratio Schedule (FR): A set number of • correct responses must be made to obtain a reinforcer Variable Ratio Schedule (VR): Varied number of correct responses must be made to get a reinforcer Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Schedules of Partial Reinforcement (cont.) • Fixed Interval Schedule (FI): The first correct • response made after a certain amount of time has elapsed is reinforced Variable Interval Schedule (VI): Reinforcement is given for the first correct response made after a varied amount of time Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.11 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.19 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Stimulus Control • Stimuli that consistently precede a rewarded • response tend to influence when and where the response will occur Operant Stimulus Generalization: Tendency to respond to stimuli similar to those that preceded operant reinforcement Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Watson & Rayner’s Research with Little Albert Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Stimulus Control (cont.) • Operant Stimulus Discrimination: Occurs • when one learns to differentiate between antecedent stimuli that signal either a reward or a nonreward Discriminative Stimuli: Stimuli that precede reinforced and nonreinforced responses Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Punishment • Punisher: Any consequence that reduces the • • • frequency of a target behavior Keys: Timing, consistency, and intensity Severe Punishment: Intense punishment, capable of suppressing a response for a long period Mild Punishment: Weak punishment; usually slows responses temporarily Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Punishment Concepts • Aversive Stimulus: Stimulus that is painful or • • • uncomfortable (e.g., a shock) Escape Learning: Learning to make a response to end an aversive stimulus Avoidance Learning: Learning to make a response to avoid, postpone, or prevent discomfort (e.g., not going to a doctor or dentist) Punishment may also increase aggression Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.22 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Cognitive Learning • Higher-level learning involving thinking, • • • knowing, understanding, and anticipating Latent Learning: Occurs without obvious reinforcement and is not demonstrated until reinforcement is provided Rote Learning: Takes place mechanically, through repetition and memorization, or by learning a set of rules Discovery Learning: Based on insight and understanding Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.23 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.24 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Modeling or Observational Learning (Albert Bandura) • Occurs by watching and imitating actions of another person or by noting consequences of a person’s actions – Occurs before direct practice is allowed • Model: Someone who serves as an example Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Steps to Successful Modeling • Pay attention to model and remember what • • • • was done Reproduce modeled behavior If a model is successful or his/her behavior is rewarded, behavior more likely to recur Once response is tried, normal reinforcement determines whether it will be repeated Bandura created modeling theory with classic Bo-Bo Doll (inflatable clown) experiments Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Figure 7.26 Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Self-Managed Behavior • Premack Principle: Any high frequency • response used to reinforce a low frequency response (e.g., no Halo 2 or GTA until you finish your homework) Self-Recording: Self-management based on keeping records of response frequencies Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 How to Break Bad Habits • Alternate Responses: Try to get the same • • • reinforcement with a new response Extinction: Try to discover what is reinforcing an unwanted response and remove, avoid, or delay the reinforcement Response Chains: Break up the chain of events that leads to an undesired response Cues and Antecedents: Try to avoid, narrow down, or remove stimuli that elicit the bad habit Psychology: A Modular Approach to Mind and Behavior, Tenth Edition, Dennis Coon Chapter 7 Behavioral Contracting • Behavioral Contract: Formal agreement • • • stating behaviors to be changed and consequences that apply; written contract State a specific problem behavior you wish to control or a goal you wish to achieve State the rewards you will get, privileges you will forfeit, or punishments you will get Type the contract, sign it, and get a person you trust to sign it