* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Social Psychology - Coweta County Schools
System justification wikipedia , lookup
Carolyn Sherif wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Social loafing wikipedia , lookup
James M. Honeycutt wikipedia , lookup
In-group favoritism wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Leon Festinger wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
Attribution bias wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Self-perception theory wikipedia , lookup
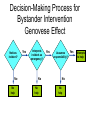
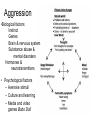
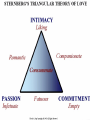
“The thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals as shaped by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others” Gordon Allport Major Themes • Human beings are social by nature • Humans are shaped by & shape society/culture • Survival tool - ability to formulate stereotypes In the beginning….. • Norman Triplett (1897) – 1st social psychological experiment [18 years after birth of psychology as science] • Interested in increased ability in presence of others • Led to complex body of literature on social facilitation •1908 with publication of Ross & McDougall’s Social Psychology text Overall framework for social psychology begins. Inspired by father of modern social psychology – Kurt Lewin Lewin proposed “formula”: “behavior is a function of the person in the environment” • Normative social influence —Conforming to group pressure out of need for acceptance or approval • Informational social influence —Conforming to group pressure out of need for direction and information • Reference Groups — People we conform to or go along with, because we like and admire them and want to be like them Conformity Key Terms • Saliency bias —tendency to focus on most noticeable factors when explaining causes of behaviors • Self-serving bias —taking credit for our successes and externalizing our failures • Attitude —learned predisposition to respond cognitively, affectively, and behaviorally to particular object • Deindividuation —Increased arousal and reduced self-consciousness, inhibition, and personal responsibility that sometimes occurs in group, particularly when members feel anonymous Group Decision Making • Groupthink —Faulty decision making that occurs when highly cohesive group strives for agreement and avoids inconsistent information Silence = Consent Group members practice Mindguarding Newly married couples Iraq war Irving Janis concept after Bay of Pigs Fiasco Group Decision Making • Group polarization —Group’s movement toward either riskier or more conservative behavior, depending on members’ initial dominant tendency (if were violent as individuals, will be violent as a group) – Is form of “confirmation bias” People can ignore stuff that contradicts what they want to be true disconfirmation bias: People overly criticize that which contradicts what they want to be true expectancy effect: People see patterns in support of their ideas where nothing actually exists status quo bias: People like to stick with what they know Group Think – Combat GT by having a “devil’s advocate” – Minority Influence: small group can get an alternate opinion out better than an individual Fundamental Attribution Error • When looking at other people’s behavior, we tend to explain it dispositionally (it’s part of person’s disposition) We tend to ignore impact of situation. • Yet, think about how we explain our own failures – do we tend to blame ourselves or something about the situation? Decision-Making Process for Bystander Intervention Genovese Effect Notices incident? No No help Yes Interprets incident as emergency? No No help Yes Assumes responsibility? No No help Yes Attempts to help • Asch Conformity Person Perception • Milgram Obedience •Festinger Cognitive Dissonance Social Comparison •Heider Balance Theory Attribution Theory •Zimbardo Prison Study •Sherif Robber’s Cave Experiment Power of the Situation • Look for consistencies in human behavior *explain behavior through internal dispositions • Social Psychologists emphasize influences/ constraints of situation • Explanations for behavior known as attributions. • Internal explanations are referred to as dispositional, external as situational Cognitive Dissonance Theory and Confirmation Bias • Confirmation bias —we tend to accept data/input that confirms what we already believe to be true • Cognitive dissonance theory —we discover inconsistencies between our attitudes and/or behaviors, we experience discomfort which we try to alleviate through attitude changes Leon Festinger's cognitive dissonance experiment, in which participants who were paid $1 to say they enjoyed a boring task, liked it better at the end of the study than those who were paid $20. People justified the lie by changing their previously unfavorable attitudes about the task (1959). Cognitive dissonance was the recital of Aesop's fable "Sour Grapes." The fox cannot get the grapes and leaves without them. He is feeling some cognitive dissonance. He wants the grapes but fails to get them. He now changes his belief about the grapes in an effort to justify his actions. He states that he now believes that the grapes are sour. Social Influence • Conformity—changing behavior as result of real or imagined group pressure • Obedience—following direct commands, usually from authority figure Obedience Factors Power of authority Distance between teacher & learner (i.e., in “shock experiment”) Assignment of responsibility Modeling/imitation Ingroups and Outgroups • Ingroup Favoritism — Viewing members more positively than members of outgroup. • Outgroup Homogeneity Effect —Judging members of more alike and less diverse than members of ingroup. History of Social Psychology Age of Activism 1960’s • Stereotyping and Prejudice – School Desegregation • Aggression - Bullet Theory • Altrusim – Bystander Intervention • Interpersonal Relations – Attraction Prejudice and Discrimination • Stereotype — belief about characteristics of people in group generalized to all members • Prejudice —learned, generally negative, attitude toward members of group • Discrimination — negative behaviors directed at members of group Aggression •Biological factors Instinct Genes Brain & nervous system Substance abuse & mental disorders Hormones & neurotransmitters • Psychological factors – Aversive stimuli – Culture and learning – Media and video games Bobo Doll James Suleiman’s Social Loafing Why Do People Loaf? VS Attraction • Physical Attractiveness (symmetry) • Proximity • Similarity Love Eros—erotic love/romantic love Philia—fraternal love (love between friends or siblings) Agape—unconditional love (companionate love) Romantic Love – Looking for Love • • • • • • • • Men Want: Physical attractiveness Ability in bed Warmth and affection Social skill Homemaking ability Dress sense Sensitivity to others’ needs • Good taste • Moral perception • Artistic creativity • • • • • • • • • • • Women Want: Record of achievement Leadership qualities Skill at the job Earning potential Sense of humor Intellectual ability Attentiveness Common sense Athletic ability Good abstract reasoning Altruism • Actions designed to help others with no obvious benefit to the helper – Egoistic model —Helping that is motivated by anticipated gain—later reciprocation, increased selfesteem, or avoidance of guilty and distress – Empathy-Altruism Hypothesis — Helping because of empathy for someone in need Helping breaks down in crowd largely due to: Diffusion of responsibility —Assuming someone else will take action (or responsibility) Genovese Effect