* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
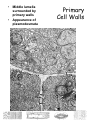
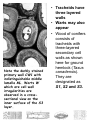
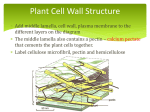
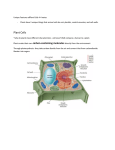
Distinguishing features of plants 1. Photosynthetic 2. Chlorophyll is photoactive pigment – typically Chl A and chl B 3. Chloroplasts – membrane bound organelle where chlorophyll is concentrated 4. Cell wall – predominantly made of polysaccharide cellulose 5. Vacuole – storage and metabolism; bounded by tonoplast membrane Plant Cells Cell wall – distinguishes plant cells from animal cells; metabolically active and/or structural Plasma membrane - surrounding the protoplast (cytoplasm) Organelles of metabolism – including, among the standard others, a variety of plastids Membrane system – synthesis and transport (ER, golgi) Nucleus – hereditary info Plant Cell Size and Longevity Cell longevity – varies from hours to millenia reproductive cells – a few hours functional dead xylem (water conducting cells) ~7000 years Cell size – minute to large cells in a region of cell division ~10 um Trachieds in pines ~10 mm Cotton fiber ~5 – 6 inches STORAGE VACUOLES Vacuoles may be the dominant feature of many cells occupying the majority of the cell volume (up to ~90%). Can be one large one or many small ones Tonoplast – single membrane enclosing vacuole Maintains homeostasis Transport proteins for nutrients and other products Mature vacuoles – contain molecules such as inorganic sugars, sugars, enzymes, organic acids, secondary compounds, etc. PLASTIDS All are maternally inherited Have their own DNA and ribosomes Divide by binary fission (like bacteria) Three typical types Chloroplast – tertiary membrane system for photosynthesis Amyloplasts – store starch Claioplasts – store oils Features of the Cell Wall 1. 2. 3. Found in all plant cells except sperm and some eggs Middle lamella – mostly pectin, cements adjacent cells together Primary cell wall Found in all plant cells Cellulose matrix with hemicellulose, proteins, pectin, lignin, cutin, and wax Characteristic of undifferentiated cells or ones that still are gorwing 4. Secondary cell wall Just inside primary cell wall Characteristic of mature cells Comprised of hemicellulose and lignin 3 layers thick • Middle lamella surrounded by primary walls • Appearance of plasmodesmata Primary Cell Walls Note the darkly stained primary wall CW1 with indistinguishable middle lamella ML. Warts W which are cell wall irregularities are observed in a crosssectional view on the inner surface of the S3 layer. • Tracheids have three layered walls • Warts may also appear • Wood of conifers consists of tracheids with three-layered secondary cell walls as shown here for ground hemlock (Taxus canadensis). They are designated as S1, S2 and S3.