* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anxiety Disorders
Symptoms of victimization wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive behavioral therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Intrusive thought wikipedia , lookup
Fragile X syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Psychological trauma wikipedia , lookup
Memory disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Selective mutism wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Claustrophobia wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Test anxiety wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
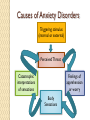
Anxiety Disorders Chapter 11 Section 2 Types of Anxiety Disorders Disorders are characterized by excessive or inappropriate anxiety reactions. Major types ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Phobias Panic disorder Generalized anxiety disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder PHOBIAS Phobias- Irrational or excessive fears of particular objects or situations. The DSM-IV classifies 3 types of phobic disorders. • Social phobia (meeting others, dating, giving speeches in class) • Specific phobia (heights, animals, insects, enclosed spaces) • Agoraphobia (open or public places) Phobia Anyone phobia? have a Phobias http://phobialist.com/ http://www.unusualphobias.com/Phobias.h tml Panic Disorder People with panic disorder experience sudden episodes of sheer terror. Characterized by intense physical symptoms (Write down 3) ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Profuse sweating Nausea Numbness or tingling Chills Trembling Chest pain Shortness of breath Rapid heartbeat Panic Disorder Panic disorder can, at first, come out of the blue. Later, they are usually associated with situations ◦ Agoraphobia can develop in people who have panic disorders. Generalized Anxiety Disorder Experience persistent anxiety that is not tied to any particular object or situation. Anxiety is a “free floating” quality that travels with the person from place to place. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Persistent obsessions and/or compulsions. Nagging, intrusive thoughts that are unable to be controlled. Compulsions are repetitive behaviors or “rituals” the person performs again and again. So… What’s the difference between a compulsion and a superstition? Causes of Anxiety Disorders Biological Factors ◦ Genetics have been found to be a cause of panic disorders, generalized anxiety disorder, OCD, and phobic disorders Causes of Anxiety Disorders Biological Factors ◦ Biochemical changes in brain trigger an “internal alarm” to induce panic ◦ Obsessional thinking may be linked to danger sensing areas of the brain may be heightened in some people. Causes of Anxiety Disorders Psychological Factors ◦ Phobias may be learned through classical conditioning (people who have been bit by dogs maybe scared of them). ◦ Operant conditioning may reinforce avoidance behavior (avoidance of object is negatively reinforced by feelings of safety). Causes of Anxiety Disorders Negative reinforcement can help perpetuate OCD (obsessive thoughts trigger anxiety, which is partially relieved through performing a ritual. In effect, the solution becomes the problem) Causes of Anxiety Disorders Triggering stimulus (internal or external) Perceived Threat Catastrophic interpretations of sensations Feelings of apprehension or worry Body Sensations