* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CELL MEMBRANE - Mrs. Guida's AP Biology Class
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
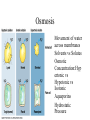
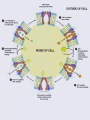
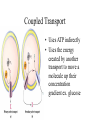
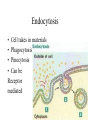
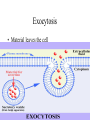
THE CELL MEMBRANE CHAPTER 5 Fluid Mosaic Model Fundamental Architecture of Cell Membranes • • • • Phospholipid Bilayer Transmembrane Proteins Interior protein Network Cell Surface Markers ( glycoproteins and glycolipids) How can we see the membrane? • Electron Microscopy • Freeze fracturing Membrane Fluidity • Saturated vs Unsaturated fats • Bacteria • Temperature Proteins in the Membrane • • • • • • Transporters Enzymes Cell surface receptors Cell surface identity markers Cell-to-cell adhesion proteins Attachments to the cytoskeleton Transmembrane Domains • Alpha Helices, span membrane at least once Pores • Betapleated sheets Passive Transport Across Membranes • Moving Down a concentration gradient • Diffusion Proteins in Diffusion • Channel Proteins • Carrier Proteins – Make membrane selectively permeable Ion Channels • Can be gates • 3 conditions determine net movement – Concentrations across membrane – Voltage difference – The state of the gate Facilitated Diffusion • Still Passive • Diffusion rate depends on the amount of available receptors • Can reach saturation • Specific to certain molecules or ions • Found in RBCs (glucose and Chloride HCO3) Osmosis • Movement of water across membranes • Solvents vs Solutes • Osmotic Concentration:Hyp ertonic vs Hypotonic vs Isotonic • Aquaporins • Hydrostatic Pressure Methods of Maintaining Balance • Extrusion- found in many single-celled eukaryotes….contractile vacoules • Isomotic Regulation- organisms that live in the ocean • Turgor- plant cells Active Transport • Uses Energy • Moves against concentration gradient • Uniporters vs symporters vs antiporters Sodium Potassium Pump Coupled Transport • Uses ATP indirectly • Uses the energy created by another transport to move a molecule up their concentration gradient ex. glucose Endocytosis • Cell takes in materials • Phagocytosis • Pinocytosis • Can be Receptor mediated Exocytosis • Material leaves the cell