* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
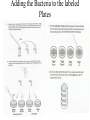
Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #10: Molecular Biology Purpose of this Lab • Learn how to insert a gene into bacteria (Heat Shock) • Analyze how a gene can transform an organism and express that gene • Provide evidence that bacteria can take in foreign DNA in the form of a plasmid • Reinforce the following process: DNA RNA Protein Trait • Observe how genes are regulated Applications of Genetic Transformation • Used in many areas of Biotechnology – – – – Agriculture (pests, frost, & drought) Bacteria (oil spills) Gene therapy (sick cells into healthy cells) Medicine (produce insulin & hormones) Key Terms to Know • • • • • • DNA: Bacteria: Growth media: Ampicillin: Arabinose: Heat shock • GFP: Plasmid E. coli (strain: HB101K-12) LB Broth (Luria & Bertani) Antibiotic kills bacteria “amp” Sugar source for energy & carbon Process that increases permeability of the cell membrane to DNA Green Fluorescent Protein (w/UV) The Genes of Interest • Ampicillin resistance • Gene regulation proteins-activate the GFP gene when arabinose is present • GFP: Green Fluorescent Protein -originally isolated from the jellyfish: Aequorea victoria Basic Process -Begin with “Starter” colonies of E. coli -Place a colony into each of the two tubes provided. labeled: -pGlo and +pGlo (yellow loop) -Add the pGlo plasmid to the +pGlo tube only (yellow loop) -Place tubes on ice (10 min) bottom of tubes should be exposed to the ice -Label the four plates as indicated in your guide -Heat Shock the tubes in water bath (50 sec.) -Return to the ice (2 min) -Add 250 L of LB broth to both tubes (sterile pipet each time) -Add 100 L of tube contents to the approriate plates -Spread the samples (w yellow loop) & tape all four plates together. Be sure your period and group name is clearly indicated. The Process of Heat Shock • Helps to increase the bacterial uptake of foreign DNA • Membrane becomes more permeable to DNA • Time is essential: -ice water bath (42ºC) for 50 sec. ice • The number of transformants should increase Adding Transformation Solution Using the Pipet Properly • Find the markings for each graduated volume on the pipet Transferring Colonies, Labeling the Plates, & Using Heat Shock Adding the Bacteria to the labeled Plates Expected Results PLATES +pGlo LB/amp +pGlo LB/amp/ara OBSERVATIONS Many colonies with white appearance Transformation observed (resistance to amp) NO fluorescence (No arabinose present) Many transformed white colonies Fluoresce bright green under UV light -pGlo LB/amp (CONTROL) No Bacterial growth present on the plate No transformation -pGlo LB only (CONTROL Bacteria present with whitish colonies (regeneration of the starter plate)