* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download f - PARNEC
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
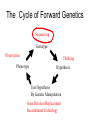
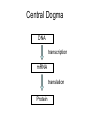
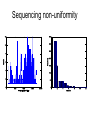
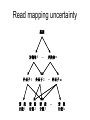
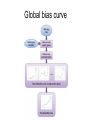
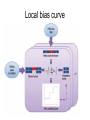
Gene expression estimation from RNA-Seq data 刘学军 2011.3.10 Outlines • • • • • Background RPKM Poisson model N-URD model Improved Poisson model The Cycle of Forward Genetics Sequencing Genotype Observation Thinking Phenotype Hypothesis Test Hypothesis By Genetic Manipulation Gene Deletion/Replacement Recombinant Technology Central Dogma DNA transcription mRNA translation Protein RNA-Seq protocal • • • • RNA is isolated from a sample. RNA is converted to cDNA fragments High-throughput sequencing Reads are mapped to a reference genome (counts of reads – ‘digital’) • Gene expression estimation An example reference ACGTCCCC 12 ACGTC reads 8 CGTCC reads 9 GTCCC reads 5 TCCCC reads This gene can be summarized by a sequence of counts 12, 8, 9, 5. Advantages of RNA-Seq • • • • Large dynamic range Low background noise Requirement of less sample RNA Ability to detect novel transcripts Challenges of RNA-Seq • Sequencing non-uniformity • Read mapping uncertainty • Paired-end sequencing data Sequencing non-uniformity Source of read mapping uncertainty • Paralogous gene family • Low-complexity sequence • Alternatively spliced isoforms of the same genes • Uncertainty in read alignment gene multireads and isoform multireads Alternatively spliced isoforms Read mapping uncertainty 基因 异构体 1 外显子 1 读 段 计数 1 … 外显子 2 读 段 计数 2 读 段 计数 3 异构体 n … 外显子 m … 读 段 计数 k Paired-end sequencing RPKM • Reads per kilobase of the transcript per million mapped reads to the transcriptome --gene expression level --isoform expression level? Mortazavi et al. (2008) Nature Methods. Jiang et al. (2009) Bioinformatics Notations: fg,i: the ith isoform of gene g. lf: isoform length kf: the number of transcript copies in the isoform The total length of the transcripts is k f l f . f F The probability of a read comes from some isoform f is kf lf pf kf lf Define f kf f F as the expression index of isoform f. k l ff f F Model assumption w: the total number of mapped reads Given a region of length l in f, the number of reads coming from that region, X ~ B w, f l which can be approximated by X ~ Pois ( w f l ) Poisson model For a gene with m exons, with lengths and n isoforms with expressions Observations Xs: number of reads mapped to an exon Poisson model For every X, the Possion parameter is where cij is 1 if isoform i contains exon j and 0 otherwise. Data likelihood, Wu et al. (2011) Bioinformatics URD model -> N-URD model Global bias curve (GBC) Local bias curve (LBC) Global bias curve Local bias curve Usage of the bias curve The N-URD models GN-URD: cij - > Gij LN-URD: cij -> Lij MN-URD: cij -> a*Gij +(1-a)*Lij 1-M: no. of iteration for LBC calculation is 1 5-M: no. of iteration for LBC calculation is 5 Li et al. (2010) Genome Biology • Use variable rates for different positions. • Poisson linear model, Non-linear model • Use empirical data to obtain the non-linear relationship between sequencing preference (ai) and the surrounding sequences. • Gene expression level with length L,