* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Asymmetries in Retrieval of Gene Function Information
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
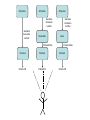
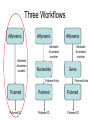
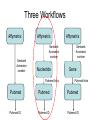
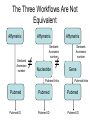
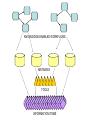
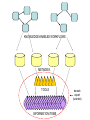
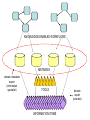
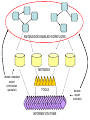
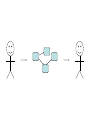
Asymmetries in Retrieval of Gene Function Information Timothy B. Patrick, PhD1, Lillian C. Folk, MS2, Catherine K. Craven, MLS3 1Healthcare Administration and Informatics, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee 2College Of Veterinary Medicine, 3Health Management and Informatics, University of Missouri-Columbia Acknowledgements • 2004 Donald A. B. Lindberg Research Fellowship • University of Missouri National Library of Medicine Biomedical and Health Informatics Research Training grant Overview • Background – What is an asymmetry in retrieval of gene function information? • Life science information retrieval and processing workflows • Example of asymmetrical workflows – Compare three apparently equivalent asymmetrical workflows • Conclusion – Documentation standards – Multidisciplinary teams for life science workflows What is an Asymmetry in Retrieval? • Taking different paths to get the same kind of information about a given biological object • Life science information retrieval and processing workflows Complex Information Retrieval • May involve the use of multiple information resources databases and analysis tools, in combination • Such combinations of resources are often represented as workflows. Workflow Standards • Business Process Execution Language for Web Services Version 1.1 – http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/library/specification/ws-bpel/ • Simple Conceptual Unified Flow Language (SCUFL) – Taverna Workbench • http://taverna.sourceforge.net/ Logical Workflows • A logical workflow is sort of like a logical process model, with processes, data links, and control links • Key aspects of the workflow are inputs, outputs and processes that transform the data Sequence ID get DNA sequence Sequence string Similarity search results Physical Workflows • A physical workflow is like a physical process model, with processes, data links, and control links UI fetch DNA sequence Sequence string BLAST BLAST results Physical Workflow Antoon Goderis, Ulrike Sattler and Carole Goble, Applying DLs to workflow reuse and repurposing Description Logics workshop, Edinburgh, Scotland, 2426 July 2005 Asymmetry • Asymmetry means the paths or workflows are different: from the same set of potential inputs about some biological object they take different paths to produce the same kind of results. • Asymmetrical workflows are equivalent if they do produce the same results. This Study • Example of asymmetrical workflows that might look to a user to be equivalent but which are not equivalent due to various features of the resources involved. • Knowledge that they are not equivalent requires knowledge of metadata about the resources. Three Workflows Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Affymetrix Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID http://www.affymetrix.com/corporate/media/genechip_essentials/gene_expression/Features_and_probes.affx http://www.mygrid.org.uk/images/pagemaster/GravesDiseasescenario_1.png http://www.mygrid.org.uk/images/pagemaster/GravesDiseasescenario_1.png Three Workflows Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Methods • We first collected representative DNA Accession numbers associated with genes expressed in a microarray experiment designed to identify changes in gene expression associated with skeletal muscle recovery from immobilization-induced sarcopenia. This experiment sought, using a mouse model, to identify differences in gene expression associated with successful recovery from sarcopenia in young muscle as compared to failed recovery in old muscle. – NIH grant AG18881 • Pattison JS, Folk LC, Madsen RW, Childs TE, Booth FW. Transcriptional profiling identifies extensive downregulation of extracellular matrix gene expression in sarcopenic rat soleus muscle. Physiological Genomics 15(1):34-43, 2003. • Pattison JS, Folk LC, Madsen RW, Booth FW. Selected Contribution: Identification of differentially expressed genes between young and old rat soleus muscle during recovery from immobilization-induced atrophy. Journal of Applied Physiology 95(5):2171-9, 2003. • Pattison JS, Folk LC, Madsen RW, Childs TE, Spangenburg EE, Booth FW. Expression profiling identifies dysregulation of myosin heavy chains IIb and IIx during limb immobilization in the soleus muscles of old rats. Journal of Physiology 553(Pt 2):35768, 2003. Methods • Next, we retrieved the Unique Identifiers (UI’s) of Entrez Pubmed citations that were associated with the Accession numbers by each of the three Entrez resources. – Directly in the case of Entrez Pubmed – Indirectly, via Pubmed links in the case of Entrez Nucleotide and Entrez Gene • Next, we compared the number of Pubmed ID's retrieved by the three resources for each of the Accession numbers. Three Workflows Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Three Workflows Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Three Workflows Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Three Workflows Affymetrix Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Genbank Accession number Nucleotide Pubmed links Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Summary of Pubmed ID’s by Accession Number # of Pubmed ID’s # of Pubmed ID’s # of Accession numbers # of Accession numbers # of Pubmed ID’s # of Accession numbers 0 198 0 132 0 216 1 36 1 112 1 34 2 10 2 5 2 0 3 4 3 2 3 1 4 1 4 0 4 0 5 2 5 0 5 0 Total 251 Pubmed Total 251 Nucleotide Total 251 Gene Methods • Compared number of Pubmed ID’s produced for each Accession number by each workflow. • Applied non-parametric test: Kendall’s W – Pubmed versus Nucleotide versus Gene – p < .05 The Three Workflows Are Not Equivalent Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Affymetrix ≠ Affymetrix Genbank Accession number Nucleotide ≠ Pubmed links Genbank Accession number Gene Pubmed links Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed Pubmed ID Pubmed ID Pubmed ID The SI field identifies secondary source databanks and accession numbers of outside resources discussed in MEDLINE articles. The field is composed of the source followed by a slash followed by an accession number and can be searched with one or both components, e.g., genbank [si], AF001892 [si], genbank/AF001892 [si]. The SI field and the Entrez sequence database links are not linked. The PubMed links to these databases are created from the reference field of the GenBank or GenPept flat file. These references include citations that discuss the specific sequence presented in these flat files. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=helppubmed.box.pubmedhelp.Box_1_Search_Field_ D#pubmedhelp.Secondary_Source_ID_ Conclusions Need for Documentation • The first conclusion I take from this project is that there is a need for documentation of workflow details. – In another study we look at the character of documentation of information processing and retrieval methods in published reports of microarray experiments Multidisciplinary Teams for Workflows • The second conclusion I take is that the development of workflows requires multidisciplinary teams. KNOWLEDGE-ENABLED WORKFLOWS METADATA TOOLS INFORMATION ITEMS KNOWLEDGE-ENABLED WORKFLOWS METADATA TOOLS INFORMATION ITEMS domain expert (scientist) KNOWLEDGE-ENABLED WORKFLOWS METADATA domain metadata expert (information specialist) TOOLS INFORMATION ITEMS domain expert (scientist) KNOWLEDGE-ENABLED WORKFLOWS METADATA domain metadata expert (information specialist) TOOLS INFORMATION ITEMS domain expert (scientist) workflows