* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MHC 2
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
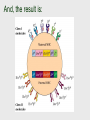
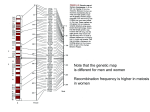
MHC diversity arises from: • Polygenicity • Polymorphism • Co-dominance • Linkage disequilibrium Polygenicity: n [ISV] (1941) : possessing any of a group of nonallelic genes that collectively control the inheritance of a quantitative character or modify the expression of a quantitative character Polymorphism: n [ISV] (1839) : the quality or state of being able to assume different forms: as a : existence of a species in several forms And by extension: existence of a gene in several forms Co-dominance: • Full expression in the heterozygous state Linkage disequilibrium: • When the observed frequencies of haplotypes in a population does not agree with haplotype frequencies predicted by multiplying together the frequency of individual genetic markers in each haplotype. http://hal.weihenstephan.de/genglos/asp/genreq.asp ?nr=519 MHC haplotypes are in disequilibrium: Two explanations are offered: 1. There has not been enough “evolutionary” time to achieve equilibrium 2. Some allelic sequences in the haplotype are adaptive (i.e., they are suited to displaying frequently occurring “foreign” peptides.) Haplotype: • Think “Polygenicity,” “polymorphism,” “co-dominance,” and “linkage disequilibrium”…. Haplotype: • Think “Polygenicity,” “polymorphism,” “co-dominance,” and “linkage disequilibrium”…. Genetic organization in the mouse is similar… continue to think about polygenicity, polymorphism, co-dominance, and linkage disequilibrium And, the result is: So… that’s the genetics… what does the synthesis of the protein look like? “Classical” and “non-classical” MHC’s “Classical” are expressed continuously. “Non-classical” are expressed in specific tissues and/or at specific times. Linkage disequilibrium (again) Some haplotypes correlate with increased incidence of disease. RR = Such association is measured by a “relative risk” factor (RR). Question: to what does “Ag+” refer?) (Ag+/Ag-) disease _____________________ (Ag+/Ag-) control MHC- III • • • • • Complement Tumor necrosis factor Heat shock proteins Hydroxylases (generally) genes related to inflammation