* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sign - GVI.cz
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
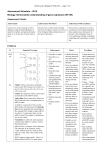
BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS Výukový materiál GE 02 - 44 Tvůrce: Mgr. Šárka Vopěnková Tvůrce anglické verze: ThMgr. Ing. Jiří Foller Projekt: S anglickým jazykem do dalších předmětů Registrační číslo: CZ.1.07/1.1.36/03.0005 Tento projekt je spolufinancován ESF a SR ČR 2014 BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS Simplified schema of protein synthesis – according to the information contained in DNA of the specific gene an RNA-fibre, which goes into the cytoplasm, where it serves as the pattern for the synthesis of the particular protein the basic concept of genetics is a gene (endowment) it was first used by W. Johannsen in 1903 gene = hereditary transferable base of a sign SIGN - PHENOTYPE signs: qualities of organisms or cells signs: a) morphological (shape and measures of the body) b) functional (ability to practise a function) c) mental (intelligence, talent, moral) SIGN - PHENOTYPE signs appear in various qualities (forms) the colour of petals can be white, yellow, …. so the colour is: a qualitative sign a monogenous sign > hereditary determined by just one gene SIGN - PHENOTYPE other signs occur in various mass, grades – quantities for example – body height, blood pressure they can be different by different people because of that these signs are called quantitative SIGN - PHENOTYPE quantitative genes are measurable they are hereditary determined by a whole group of genes each gene has just a small effect > polygenous signs GENE - GENOTYPE signs like that are not transferred from parents to descendants like that only endowments are transferred endowments – hereditary premises of signs endowments – information for creation of signs GENE - GENOTYPE material carrier of signs are genes genes: specifically delimited sections of nucleic acids they determinate signs in their particular qualities and quantities they occur in two or more particular forms, shapes = alleles GENE - GENOTYPE the complex of all genes in particular alleles is called its genotype genotype is always a wider complex than phenotype genotype determines extension, mass of phenotype possibilities of its carrier GENE - PHENOTYPE factors of environment can initiate, suppress or modify some parts of genetic programme, it means adapt them a standard sign cannot develop without a genetic base by any organism the mass of heredity determination by any sign = degree of heritability genotype + environment = phenotype WORKSHEET Simplified schema of protein synthesis – according to the information contained in DNA of the specific gene an RNA-fibre, which goes into the cytoplasm, where it serves as the pattern for the synthesis of the particular protein COMPLETE THE PICTURE SOURCES ŠMARDA, Jan. Genetika: pro gymnázia. 1. vyd. Praha: Fortuna, 2003, 143 s. ISBN 80-7168851-7.