* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C8 Challenge
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
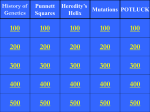
Chapter 8: Microbial Genetics DNA Protein Synthesis Regulation of Bacterial Genes Mutation Genetic Transfer $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 FINAL ROUND © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $100 Question A sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product is a(n) a. b. c. d. genetic code. gene. codon. anticodon. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $100 Answer A sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a functional product is a(n) a. b. c. d. genetic code. gene. codon. anticodon. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $200 Question Which process results in a new doublestranded DNA molecule that contains one original strand and one new strand? a. b. c. d. transformation transcription semiconservative replication translation ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $200 Answer Which process results in a new doublestranded DNA molecule that contains one original strand and one new strand? a. b. c. d. transformation transcription semiconservative replication translation BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $300 Question In DNA replication, the newly added nucleotide is joined to the growing DNA strand by a. b. c. d. DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase. DNA ligase. DNA gyrase. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $300 Answer In DNA replication, the newly added nucleotide is joined to the growing DNA strand by a. b. c. d. DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase. DNA ligase. DNA gyrase. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $400 Question DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the _____ end only on a DNA strand. a. b. c. d. 2′ 3′ 4′ 5′ ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $400 Answer DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the _____ end only on a DNA strand. a. b. c. d. 2′ 3′ 4′ 5′ BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $500 Question Which of the following enzymes joins DNA strands and joins Okazaki fragments and new segments in excision by forming covalent bonds? a. b. c. d. RNA polymerase DNA polymerase DNA ligase DNA gyrase ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 1: DNA $500 Answer Which of the following enzymes joins DNA strands and joins Okazaki fragments and new segments in excision by forming covalent bonds? a. b. c. d. RNA polymerase DNA polymerase DNA ligase DNA gyrase BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $100 Question What carries the coded information for making specific proteins from DNA to ribosomes? a. b. c. d. mRNA rRNA tRNA RNA polymerase ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $100 Answer What carries the coded information for making specific proteins from DNA to ribosomes? a. b. c. d. mRNA rRNA tRNA RNA polymerase BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $200 Question Which molecules recognize specific codons and transport amino acids? a. b. c. d. DNA mRNA rRNA tRNA ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $200 Answer Which molecules recognize specific codons and transport amino acids? a. b. c. d. DNA mRNA rRNA tRNA BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $300 Question A group of three nucleotides is called a(n) a. b. c. d. codon. anticodon. exon. intron. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $300 Answer A group of three nucleotides is called a(n) a. b. c. d. codon. anticodon. exon. intron. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $400 Question Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at the a. b. c. d. intron. mRNA. tRNA. promoter. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $400 Answer Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at the a. intron. b. mRNA. c. tRNA. d. promoter. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $500 Question Of the 64 codons, how many are sense codons? a. b. c. d. 48 60 61 52 ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 2: Protein Synthesis $500 Answer Of the 64 codons, how many are sense codons? a. b. c. d. 48 60 61 52 BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $100 Question Perhaps 60–80% of genes are NOT regulated, but are a. b. c. d. constitutive. continuous. degenerative. repressed. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $100 Answer Perhaps 60–80% of genes are NOT regulated, but are a. b. c. d. constitutive. continuous. degenerative. repressed. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $200 Question What is the process that turns on the transcription of a gene or genes? a. b. c. d. induction repression translation catabolite repression ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $200 Answer What is the process that turns on the transcription of a gene or genes? a. b. c. d. induction repression translation catabolite repression BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $300 Question A set of operator and promoter sites and the structural genes they control defines a. b. c. d. a corepressor. an operon. an inducer. cAMP. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $300 Answer A set of operator and promoter sites and the structural genes they control defines a. b. c. d. a corepressor. an operon. an inducer. cAMP. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $400 Question Inhibition of the metabolism of alternative carbon sources by glucose is called a. b. c. d. induction. repression. corepression. catabolite repression. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $400 Answer Inhibition of the metabolism of alternative carbon sources by glucose is called a. b. c. d. induction. repression. corepression. catabolite repression. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $500 Question Epigenetic inheritance is a. a process that turns on the transcription of a gene (or genes). b. the semiconservative replication of DNA to be passed on to offspring. c. turning genes off by methylation of certain nucleotides. d. a process that inhibits gene ANSWER expression. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 3: Regulation of Bacterial Genes $500 Answer Epigenetic inheritance is a. a process that turns on the transcription of a gene (or genes). b. the semiconservative replication of DNA to be passed on to offspring. c. turning genes off by methylation of certain nucleotides. d. a process that inhibits gene expression. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $100 Question Ionizing radiation causes a. b. c. d. DNA to break. bonding between adjacent thymines. nitrogenous base substitutions. the formation of highly reactive ions. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $100 Answer Ionizing radiation causes a. b. c. d. DNA to break. bonding between adjacent thymines. nitrogenous base substitutions. the formation of highly reactive ions. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $200 Question Ultraviolet light is a form of mutagenic radiation, which causes cellular damage that can be a. b. c. d. repaired by DNA replication. repaired during transcription. repaired during translation. cut out and replaced. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $200 Answer Ultraviolet light is a form of mutagenic radiation, which causes cellular damage that can be a. b. c. d. repaired by DNA replication. repaired during transcription. repaired during translation. cut out and replaced. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $300 Question What is the most common type of mutation involving single base pairs? a. b. c. d. frameshift mutation nonsense mutation missense mutation base substitution ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $300 Answer What is the most common type of mutation involving single base pairs? a. b. c. d. frameshift mutation nonsense mutation missense mutation base substitution BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $400 Question Mutations in which one or a few nucleotide pairs are deleted or inserted in the DNA are called a. b. c. d. nonsense mutations. frameshift mutations. point mutations. base-pair mutations. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $400 Answer Mutations in which one or a few nucleotide pairs are deleted or inserted in the DNA are called a. b. c. d. nonsense mutations. frameshift mutations. point mutations. base-pair mutations. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $500 Question Approximately what percentage of substances found by the Ames test to be mutagenic have been found to be carcinogenic in animals? a. b. c. d. 85% 75% 95% 90% ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 4: Mutation $500 Answer Approximately what percentage of substances found by the Ames test to be mutagenic have been found to be carcinogenic in animals? a. b. c. d. 85% 75% 95% 90% BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $100 Question Which of the following is defined as the “exchange of genes between two DNA molecules to form new combinations of genes on a chromosome”? a. b. c. d. conjugation transduction genetic recombination crossing over ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $100 Answer Which of the following is defined as the “exchange of genes between two DNA molecules to form new combinations of genes on a chromosome”? a. b. c. d. conjugation transduction genetic recombination crossing over BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $200 Question Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell a. b. c. d. by a bacteriophage. as naked DNA in solution. by sexual reproduction. by crossing over. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $200 Answer Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell a. b. c. d. by a bacteriophage. as naked DNA in solution. by sexual reproduction. by crossing over. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $300 Question The process in which bacterial DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a recipient cell inside a bacteriophage is called a. b. c. d. conjugation. transduction. specialized transduction. transformation. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $300 Answer The process in which bacterial DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a recipient cell inside a bacteriophage is called a. b. c. d. conjugation. transduction. specialized transduction. transformation. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $400 Question The process in which genetic material is transferred from one bacterium to another is called a. b. c. d. conjugation. transformation. replication. specialized transduction. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $400 Answer The process in which genetic material is transferred from one bacterium to another is called a. b. c. d. conjugation. transformation. replication. specialized transduction. BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $500 Question Which type of plasmid carries genes for sex pili and for the transfer of the plasmid to another cell? a. b. c. d. resistance factors bacteriocin plasmids conjugative plasmids transposons ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Topic 5: Genetic Transfer $500 Answer Which type of plasmid carries genes for sex pili and for the transfer of the plasmid to another cell? a. b. c. d. resistance factors bacteriocin plasmids conjugative plasmids transposons BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. FINAL ROUND Question What provides a natural mechanism for the movement of genes from one region of a DNA molecule to another? a. b. c. d. operons transposons plasmids R factors ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. FINAL ROUND Answer What provides a natural mechanism for the movement of genes from one region of a DNA molecule to another? a. b. c. d. operons transposons plasmids R factors BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.