* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetically Modified Foods and Organisms
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
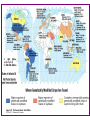
Genetically Modified Foods and Organisms Traditional plant breeding DNA is a strand of genes, much like a strand of pearls. Traditional plant breeding combines many genes at once. Commercial variety Traditional donor New variety (many genes are transferred) X = (crosses) Desired Gene Desired gene Plant biotechnology Using plant biotechnology, a single gene may be added to the strand. Desired gene Commercial variety New variety (only desired gene is transferred) = (transfers) Desired gene Traditional breeding involves exchanging all genetic material between two related plants. Genetic engineering usually only involves moving one or two genes and can cross the species barrier. Biotechnology • Manipulation and management of biological organisms • • • • Recombinant DNA techniques Tissue culture (cloning) Cell fusion Embryo transfer • Positive: high yielding, disease resistant “super” plants • Negative: periphery excluded by distance and cost + concerns about safety More than 50 biotech food products have been approved for commercial use in the United States • Canola • Corn • Cotton • Papaya • Potato • Soybeans • Squash • Sugarbeets • Sweet corn • Tomato Four crops accounted for nearly all of the global biotech crop area in 2002 Soybeans 62% Corn 21% Cotton Canola 12% 5% Source: International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications Four countries accounted for 99 percent* of the global biotech crop area in 2002 United States 66% Argentina Canada China 23% 6% 4% *Australia, Bulgaria, Colombia, Germany, Honduras, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Romania, South Africa, Spain and Uruguay accounted for the remaining 1 percent of biotech crop acres. Source: International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications Some Benefits of Genetically Modified Foods Some Concerns about Genetically Modified Foods • • • • • • • • Possible adverse effects on human health Introduction of new allergens Antibiotic-resistant genes in foods Production of new toxins Concentration of toxic metals Enhancement of toxic fungi Environmental impacts Dangers not yet identified http://www.ucsusa.org/food_and_environment/