* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
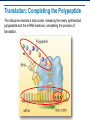
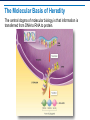
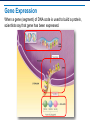
Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis Learning Objectives Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. Describe the central dogma of molecular biology. The Genetic Code RNA has four bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil. These bases form a “language”: A, C, G, and U. The Genetic Code: Codons The genetic code is read in three-letter groupings called codons. A codon is a group of three nucleotide bases in messenger RNA that specifies a particular amino acid. AUG AAC UCU Genetic Code Table There are 64 possible three-base codons in the genetic code. Reading Codons Start at the middle of the circle with the first letter of the codon and move outward. CAC = Histidine Start and Stop Codons The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons AUG = methionine = “start” codon Translation Transcribed mRNA directs the translation process. Translation is the process that makes proteins using the copy of the DNA code on the mRNA. Translation: Transfer RNA To start translation, tRNA molecules bind to mRNA codons, carrying amino acids with them. anticodon Translation: The Polypeptide Assembly The ribosome helps form a peptide bond. It breaks the bond holding the first tRNA molecule to its amino acid. Translation: Completing the Polypeptide The ribosome reaches a stop codon, releasing the newly synthesized polypeptide and the mRNA molecule, completing the process of translation. Roles of RNA in Translation All three major forms of RNA—mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA—are involved in the process of translation. The Molecular Basis of Heredity The central dogma of molecular biology is that information is transferred from DNA to RNA to protein. Gene Expression When a gene (segment) of DNA code is used to build a protein, scientists say that gene has been expressed.