* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
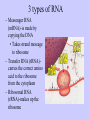
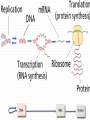
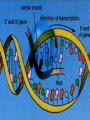
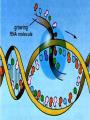
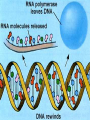
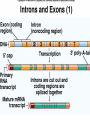
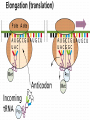
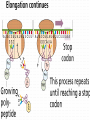
Protein Synthesis-How do we go from genotype to phenotype Nucleic Acids Differences RNA DNA • Single strand • Has Us • Can leave the nucleus • Ribose sugar • Double stranded helix • Has Ts • Stays only in the nucleus • Deoxyribose sugar 3 types of RNA – Messenger RNA (mRNA)-is made by copying the DNA • Takes strand message to ribosome – Transfer RNA (tRNA)carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome from the cytoplasm – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)-makes up the ribosome Transcription • Where: Nucleus • What: takes the DNA message and makes mRNA • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA TRANSCRIBE THESE ON YOUR NOTEGUIDE. • ATCAT TCGGGAT UAGUAAGCCCUA • CCATTACGGGA GGUAAUGCCCU SPLICING Before the mRNA can go to the ribosome, it needs to be spliced. – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. Translation • Where: ribosome • What: tRNA brings in amino acids to the ribosome – tRNA anticodon: 3 bases that are complementary to mRNA • All mRNA start with the codon AUG • Protein Synthesis stops when a stop codon is reached. What determines what amino acid is attached to the tRNA? • Is it mRNA or tRNA? mRNA Watch the animation. http://www.wisconline.com/objects/index.asp?objID=AP1302 Does it matter what order the amino acids are in? • The order of amino acids dictates the shape of the protein. • The shape determines the function of the protein. • Wrong order, wrong shape, no function • http://www.lewport.com/10712041113402793/lib/10712041113402 793/Animations/Protein%20Synthesis%20%20long. swf Write the anticodons for the codons • AUGCAUUAGGCCAU UACGUAAUCCGGUA • CGAAUACAGGAU GCUUAUGUCCUA Write the amino acid sequence from the mRNA sequence. • AUGCAGCAUUAUACC Methionine glutamine histidine tyrosine threonine • CGAAUACAGGAU Arginine isoleucine glutamine aspartic acid