* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S-strain (virulent)
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
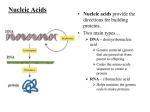
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Griffith took the 1st steps in answering whether genes are made of DNA or Protein. Used bacteria to help solve this problem. S-strain (virulent) - Coated with mucus and caused pneumonia R-strain (avirulent) - no mucus and did not cause pneumonia Griffith’s Experiment These results led Griffith to believe that some material from the S-strain was transferred to the R-strain, which converted the R-strain to s-strain. Transformation - the process during which bacteria are changed by absorbing genetic material from an outside source. Griffith was still not sure whether it was DNA or Protein being transferred. Chase and Hershey used bacteriophages (phages) to prove whether protein or DNA is the genetic material. The Experiment 1. Radioactive DNA was put in one group of phages and radioactive protein was put into another group of phages. 2. The phages were used to infect the bacteria. 3. Radioactivity was only found in bacteria infected by DNA. 4. DNA is the genetic material. Chargaff’s Rule The amount of adenine in DNA is always equal to the amount of thymine. %A = %T The amount of cytosine in DNA is always equal to the amount of guanine. %C = %G •Discovered by Watson and Crick •Consist of long strands of nucleotides •Deoxyribose •Phosphate group •Nitrogenous bases Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine The nitrogenous bases are divided into two groups. Purines - include adenine and guanine. They have two rings. Pyrimidines - include cytosine and thymine. They are smaller and have only one ring. Has a sugar phosphate backbone on the outside (sides of the ladder) Bases face inward toward the center and meet each other in pairs (rungs of the ladder). The bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. Adenine - Thymine Cytosine - Guanine double bond triple bond The process by which DNA makes copies of itself (Interphase of Cell Division) 1. Double helix unwinds 2. Hydrogen bonds are broken 3. The two strands break apart, like a zipper 4. New nucleotides begin to attach to the original DNA 5. This will form two new DNA molecules This is semiconservative replication, because each new strand is half comprised of molecules from the old strand. DNA is a code (set of blueprints) for making protein. Protein synthesis is the process that manufactures proteins. RNA Nucleic Acid •Single stranded •4 Bases Adenine Cytosine •Ribose sugar Guanine Uracil Messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries the coded instructions for protein synthesis from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) Brings amino acids to the ribosome in the correct order so that they can be built into the new protein. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Make up the structure of a ribosome, along with several proteins.