* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
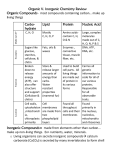
Have out: Week #9 (9/14-9/18) Warm Up – Mon, 9/14: Chemistry of Life notes (Pg. 3) Compounds foldable (Pg. 9) - Special Chemicals of Life video clip Biology Fun Fact: Today’s Learning Targets: - Describe the difference between an organic & inorganic compound. - Identify & explain the molecular structure of the 4 macromolecules necessary for life. Homework: Agenda: 1. Acids & Bases lecture 2. Inorganic & Organic Compounds needed for life 1. Study for the Biochemistry Unit Test – Wed, 9/16 & Thurs, 9/17 Unit Learning Goal: I will understand the atomic & molecular structures that are required by all forms of life. Pg. 3 – Unit 2: Chemistry of Life note packet The pH of Nature video clip Acids & Bases Solutions (solute + water) can be determined to be either an acid or a base. Here how it works… A few (1 in 550 million) water molecules spontaneously split into ions. ◦ Pure water has equal amounts of H+ & OHions. This is considered neutral. ◦ Acids have higher amounts of H+ ions. (#26) ◦ Bases have higher amounts of OH- ions. (#27) pH measures the concentration of hydrogen (H) ions in a solution. ◦ Lower pH means a higher concentration of H+ ions (#28) Pg. 3 – Unit 2: Chemistry of Life note packet What is pH? The pH scale is used to measure the relative acidity or alkalinity of solutions. (#28) ◦ 7 (middle of the scale) is considered neutral. ◦ Anything approaching zero (0-6.9) is more acidic. ◦ Anything approaching 14 (7.1-14) is more basic or alkaline. (#29) Pg. 3 – Unit 2: Chemistry of Life note packet What is pH? “pH” stands for the potential/power of Hydrogen. pH is a logarithmic scale, meaning that an change of 1 pH is actually a tenfold increase or decrease in the H+ concentration of the solution. (#30) ◦ Beer is 10 times (101) more acidic than tomatoes. ◦ Stomach acid is 1000 (103) more acidic than tomatoes. Pg. 3 – Unit 2: Chemistry of Life note packet pH & Homeostasis Blood requires a pH of 7.35-7.45. ◦ Acidic, basic or neutral? Sweat has a pH between 4.0-6.8. ◦ Acidic, basic or neutral? Saliva pH is normally around 6.0. ◦ Acidic, basic or neutral? Blood & other body fluids contain buffers, which can “absorb” increases on H+ (acid) or OH- (base) ions. ◦ This keeps blood pH within a narrow range, no matter how acidic or alkaline your diet is. Organism (You & me) Levels of Organization of Life Tissue (Muscle) Cell (Nerve Cell) Organelle (Nucleus) Molecule & Compounds (Amino Acid) Special Chemicals of Life (2 mins) The Special Chemicals of Life video clip As you watch the following video, listen for the necessary chemicals “for life” to exist on Earth. Write down these chemicals in your Warm-up box for TODAY! Week #9 (9/14-9/18) Have out: - Biochemistry Unit Pre-Test Re-visit Pick up: Warm Up – Tues, 9/15: Biology Fun Fact: Biochemistry plays an important role in forensic science, allowing investigators to seek out criminals based on DNA evidence. The first person convicted of a crime through DNA evidence took place in 1988; his name was Colin Pitchfork, a convicted rapist & murderer. Agenda: Today’s Learning Target: - Review all Objectives of the Biochemistry Unit 1. Finish Organic v. Inorganic notes – foldable 2. Review for Biochemistry Unit Exam - Organic Molecules Review wkst/Concept Map Compounds foldable Glue stick & scissors Organic Molecules Concept Map/Review (Pg. 10) Homework: 1. Study for the Biochemistry Unit Test – Wed, 9/16 & Thurs, 9/17 - Complete your OM Concept Map/Review! Unit Learning Goal: I will understand the atomic & molecular structures that are required by all forms of life. Pg. 9 – Compounds Foldable Organic vs. Inorganic COMPOUNDS Organic compounds – compounds with a Carbonbased core that are produced by living organisms (plants or animals) • Usually contain hydrogen (H), carbon (C), oxygen (O) & nitrogen (N) together in large molecules called macromolecules • Cells (life) are made of these compounds • Carbon atoms enable these compounds to bond over & over in long durable chains ◦ Examples: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids Per.4 Pg. 9 – Compounds Foldable Organic vs. Inorganic COMPOUNDS Inorganic Compounds – compounds that do NOT contain carbon (C) & hydrogen (H) together Examples: water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), salts (NaCl) Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable Per. 1 CARBOHYDRATES Includes: sugars, starches & cellulose ◦ Classified according to size ◦ Monosaccharides—simple sugars ◦ Ie., fruits (fructose) ◦ Plants produce it during photosynthesis ◦ Main source of energy for animals Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable CARBOHYDRATES Includes: sugars, starches & cellulose ◦ Classified according to size ◦ Disaccharides—2 simple sugars joined by dehydration synthesis (loss of water molecule) ◦ I.e., Table sugar (sucrose = glucose + fructose) Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable CARBOHYDRATES Includes: sugars, starches & cellulose ◦ Classified according to size ◦ Polysaccharides—long-branching chains of many linked simple sugars (complex carbohydrates) ◦ I.e, Potatoes & grains (starch) ◦ Plants maintain their physical structures (cell walls) with the help of cellulose ◦ Animals store energy in the form of glycogen or animal starch Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable LIPIDS Include: fats, waxes, steroids & phospholipids Cells use lipids to build membranes & protective layers, to store energy & to communicate among different parts of cell Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable LIPIDS Phospholipids: specific type of lipid •Head of the molecule is “polar” & is hydrophilic (water-loving) •Tail of the molecule is “nonpolar” & is hydrophobic (water-fearing) Per.3, 4 •This combination is crucial (VITAL, NECESSARY, CRITICAL, WITHOUT IT YOU ARE DEAD) to cell function!!! Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable NUCLEIC ACIDS Contain all instructions for growth, repair & replication of cells ◦ Provide “blueprint for life” Week #9 (9/14-9/18) Have out: - Compounds Concept Map (Pg. 11) (they will be graded this hour) Warm Up – Wed, 9/16 & Thurs, 9/17: Biology Fun Fact: Although there are 92 naturally occurring elements, only about 24 of them are necessary to living things. Most of the rare or non-naturally occurring elements are obviously not important to biological life. Today’s Learning Target: - Exhibit mastery of all Objectives of the Biochemistry Unit on the Exam Your Science Ntbks Pick up: Compounds Concept Map (Pg. 11) Glue stick & scissors Biochemistry Exam Answer Sheet (Pg. 12) Agenda: 1. Finish Organic Compounds foldable 2. Biochemistry Unit Exam 3. Begin Cell Unit with Cell Unit Pre-Test (if time) Homework: None Unit Learning Goal: I will understand the atomic & molecular structures that are required by all forms of life. Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable NUCLEIC ACIDS Types: ◦ Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ◦ Ribonucleic acid (RNA) ◦ Composed of Nucleotide bases A = Adenine G = Guanine C = Cytosine T = Thymine U = Uracil (only found in RNA) ◦ DNA & RNA work together to make proteins Per. 1 Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable PROTEINS Extremely long folded molecules built out of units called amino acids linked together by peptide bonds Provides structure for cells & tissues (like muscles) Human body has about 2,000 different types of proteins ◦ All are built from combinations of 20 amino acids Pg. 9 – Organic Compounds Foldable PROTEINS Did you know? Sickle cell anemia (blood disorder) & several cancers result from a single change in the amino acid sequence of proteins! Types of Proteins: ◦ Enzymes: a catalyst, speeds up chemical reactions by lowering the amount of energy needed ◦ Collagen: found in cartilage, bones & tendons ◦ Keratin: found in hair & nails AND THESE ARE JUST 3 EXAMPLES OF THE OVER 2,000!!!! Pg. 11 – Compounds Concept Map Concept Map Find some with the SAME COLOR OUTFIT as you today! Take with you your Compounds foldable, your Biochemistry Concept Map & a writing device! Using the notes in your Compounds foldable, complete the Compounds Concept Map. Be prepared to share your Answers! Pg. 1 – Biochemistry Unit Pre-Test Biochemistry Unit Learning Goal & Scales Learning Goal: I will understand the atomic & molecular structures that are required by all forms of life. ◦ Students will be able to: ◦ Identify the nine basic levels of organization of life. ◦ Describe the difference between matter & energy. ◦ Identify the three subatomic particles of an atom & their corresponding electrical charges. ◦ Describe the basic difference between ionic, covalent & hydrogen bonds. ◦ Describe the difference between an organic & inorganic compound. ◦ Identify & explain the molecular structure of the four macromolecules necessary for life. Pg. 1 – Biochemistry Unit Pre-Test Biochemistry Unit Pre-Test & Study Guide Re-read through each Unit Objectives If you are SUPER DUPER CONFIDENT & CAN APPLY/EXPLAIN AN EXAMPLE for that objective, draw a blue SMILEY FACE (4) in that square. If you are CONFIDENT that you know/can do that objective, put a green CHECK MARK (3) in that square. ◦ GO! ‘cause you KNOW! If you HAVE HEARD OF/KIND OF KNOW that objective, put a yellow STAR (2) in that square. ◦ HAULT or WAIT…not sure! If you HAVE NEVER HEARD OF/DO NOT KNOW that objective, put a red QUESTION MARK (1,0) in that square. ◦ STOP! I have no idea! Pg. 10 – Biochemistry Concept Map/Review Concept Map & Review Find some with the SAME COLOR EYES as you today! Take with you your Compounds foldable, your Biochemistry Concept Map/Review & a writing device! Using the notes in your Compounds foldable, complete the Biochemistry Concept Map/Review. Be prepared to share your Answers! Pg. 12 – Biochemistry Unit Exam Unit Exam Have out your Biochemistry Concept Map. ◦ Let’s have a look at the correct answers to complete the flow-chart. You may use your Science Ntbk as a resource while you test for the first 10 mins of testing time. After 10 mins, you will turn in your Science Ntbk to be GRADED at Lab 4. NO TALKING! Talking = Cheating = “0” When finished with your Exam, turn in your Answer Sheet & Exam at the FRONT teacher station. ◦ Pick up/get out… ◦ a new Section Divider for your Sci. Ntbk & label it “The Cell Unit”, ◦ The Cell Unit Pre-Test – Pg. 1 (read the Objectives & rate yourself) & ◦ 4 crayons Organism (You & me) Levels of Organization of Life Tissue (Muscle) Cell (Nerve Cell) Organelle (Nucleus) Molecule & Compounds (Amino Acid) How do Biochemists ACTUALLY know… that there are molecules, compounds & macromolecules that make up a cell’s structures (organelles)? Can they see these structures? Pg. 1 – “The Cell Unit Pre-Test” Cell Structure & Function Unit Learning Goal & Scales Learning Goal: I will understand the basic components of the cell & how they function. ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Identify various characteristics that set living organisms apart from non-living matter. Correctly label the parts of a microscope. Describe the function of each microscope part & correctly use each part for its appropriate purpose. Distinguish between a prokaryotic & eukaryotic cell. Distinguish between a plant & animal cell. Identify the major cell organelles that allow for a cell to function properly. Describe the function of each major cell organelle. Describe the structure & function of the phospholipid bilayer of a cell. Distinguish between the cell membrane transport mechanisms of osmosis & diffusion. Distinguish between passive & active forms of cell transport. Describe what an isotonic, hypotonic & hypertonic solution is. & what will happen to a cell is each kind of solution. ◦ Logically justify what will happen to a cell is each kind of solution. Pg. 1 – “The Cell Unit Pre-Test” Cell Structure & Function Unit Pre-Test (& Study Guide) •Read through each Unit Objectives •If you are SUPER DUPER CONFIDENT & CAN APPLY/EXPLAIN AN EXAMPLE for that objective, draw a blue SMILEY FACE (4) in that square. •If you are CONFIDENT that you know/can do that objective, put a green CHECK MARK (3) in that square. ◦ GO! ‘cause you KNOW! •If you HAVE HEARD OF/KIND OF KNOW that objective, put a yellow STAR (2) in that square. ◦ HAULT or WAIT…not sure! •If you HAVE NEVER HEARD OF/DO NOT KNOW that objective, put a red QUESTION MARK (1,0) in that square. ◦ STOP! I have no idea! Week #9 (9/14-9/18) Have out: - The Martian & the Car Pick up: Warm Up – Fri, 9/18: Biology Fun Fact: Moths taste with their feet. Atlas moth is the largest Lepidoptera in the world with 65 in2 wingspan. Your Science Ntbk The Martian & the Car (Pg. 2) Getting to Know the Microscope wkst (Pg. 3) Today’s Learning Targets: -Identify various characteristics that set living organisms apart from non-living matter. - Correctly label the parts of a microscope. - Describe the function of each microscope part & correctly use each part for its appropriate purpose. Agenda: 1. Getting to Know the Microscope wkst Homework: 1. Complete Getting to Know the Microscope wkst (if needed) – Mon, 9/21 Unit Learning Goal: I will understand the basic components of the cell & how they function. Pg. 2 - Martian & the Car The Martian & the Car Let’s read through the scenario together. Now put yourself in 2 different sets of shoes: ◦ Prosecutor (LEFT SIDE OF CLASS – near the FRONT door) ◦ Marvin the Martian has NOT found “life” (the car) ◦ Defense Attorney (RIGHT SIDE OF CLASS – near the SIDE door) ◦ Marvin the Martian HAS found “life” (the car) Be prepared to discuss/debate your ideas next class! Pg. 3 - “Getting to Know the Microscope” wkst Complete your “Getting to Know the Microscope” wkst (Pg. 3) using the colored pencils/markers. Microscope Quiz – Fri, 9/25 - Be able to identify & name the parts of a microscope CORRECTLY (spelling is important!) - Be able to describe what each part does for seeing a specimen under the microscope