* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TwoQuestions Darwin Could Not Answer
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
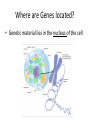
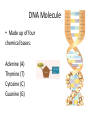
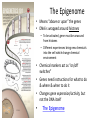
What are Genes? • Stretches of DNA molecules that carry the instructions for building a living thing • DNA as “blue print” Where are Genes located? • Genetic material lies in the nucleus of the cell What are Chromosomes? • Coiled strands of DNA molecules • Carry genetic information/instructions DNA Molecule • Made up of four chemical bases: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Function of DNA: Making Proteins • Bases group together to form a codon • Each codon (word) creates a specific amino acid Making Proteins, Cont. • A string of amino acids (sentence) makes a specific protein • Proteins determine what an organism will look like Function of DNA: Replication • To be passed down generation to generation, each cell must contain ALL genetic info to build & maintain cells DNA Replication • • • • A – T (Adenine – Thymine) C – G (Cytosine – Cytosine) Splits in half at base pairs Rebuilds the other side Mitosis • Division & replication of somatic (regular) cells (Ex: skin cells, bone cells) • Somatic cells are diploid (contain 2 chromosomes) 46 46 46 46 46 46 46 Meiosis • Production of reproductive cells (gametes) – Sperm in males; Eggs in females • Gametes are haploid (have only 1 chromosome) Recombination • New genetic combinations as a result of sexual reproduction = VARIATION The Epigenome • Means “above or upon” the genes • DNA is wrapped around histones – To be activated, gene must be unwound from histones – Different experiences bring new chemicals into the cell which change chemical environment • Chemical markers act as “on/off switches” • Genes need instructions for what to do & where & when to do it • Changes gene expression/activity, but not the DNA itself • The Epigenome The Epigenome • Genes have a lot more plasticity (ability to be altered for good or bad) than previously thought • This plasticity responds directly to environmental inputs – Based on people’s experiences • Stress, exposure to toxic chemicals, diet, etc. • CAN occur during an individual’s lifetime and may affect offspring & future generations “Epigenetics is proving we have some responsibility for the integrity of our genome”