* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Review - Chemistry Courses: About: Department of
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
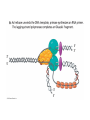
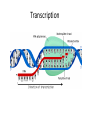
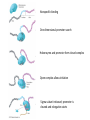
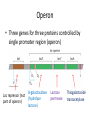
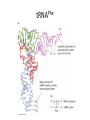
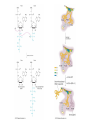
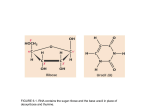
Final Review C483 Spring 2013 Replication Transcription Nonspecific binding One-dimensional promoter search Holoenzyme and promoter form closed complex Open complex allows initiation Sigma subunit released; promoter is cleared and elongation starts Eukaryotic Transcription • Multiple RNA Polymerases— compartmentalization • General Transcription Factors • Role of Chromatin • mRNA processing Operon • Three genes for three proteins controlled by single promoter region (operon) Lac repressor (not part of operon) B-galactosidase (hydrolyse lactose) Lactose permease Thiogalactoside transacetylase Translation Overview • Genetic Code • tRNA structure • Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase • Ribosome structure • Next lecture: initiation, elongation, termination tRNAPhe Question Distribution • Comprehensive (chapters 1-19) – Approximately 2-3 questions/chapter – Study questions from lectures – Major in the majors – Be able to apply major principles • Chapters 20-22 – Approximately 5-6 questions per chapter Chapter Overviews 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Compartmentalization IMF, acid/base, pH and buffers Amino acids and primary structure Protein structure and Hemoglobin Enzyme kinetics, Inhibitors, allosteric Catalytic mechanisms, serine protease 7. Function of coenzymes 8. Structure of carbohydrates 9. Membranes and signal transduction 10.Free energy, standard free energy, ATP 11.Glycolysis chemistry, energy, purpose, regulation 12.Gluconeogenesis, PPP, glycogen metabolism chemistry, energy, purpose, regulation 13.Citric acid cycle chemistry, energy, purpose, regulation 14.Electron transport, ATP synthase, P/O ratio 15. purpose of light reactions, dark reactions 16. energetics of FA synthesis and degradation 17. nitrogen processing, catabolism of AA 18. medical applications of nucleotide metabolism 19. nucleic acid structure on atomic level Major Principles • • • • • • • Chemical Structure Structure-Function relationship Thermodynamics of reactions Kinetics (catalysis) of reactions Cofactors and high energy bonds Purpose/outcomes of process Regulation of pathway related to purpose Major Enzymes • You should be able to figure out what many enzymes do by their names IF you know your basic biochemistry – Substrate structures – Dehydrogenase, carboxylase, kinase, protease, phosphorylase, phosphatase Key Metabolites • Know structures; associate with pathway • Glucose, glucose-6-P, DHAP, PEP, pyruvate, acetyl CoA, ribulose, UDP-glucose, glycogen, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • Amino acids, nucleotides