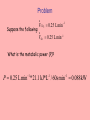* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Metabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
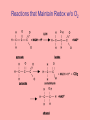
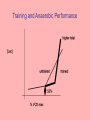
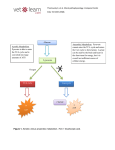
Wed Sept 12 & Friday Sept 14 Problem Suppose the following: V CO2 0.25 L min 1 V O2 0.25 L min 1 What is the metabolic power (P)? 1 1 P 0.25 L min * 21.1 kJ*L / 60smin 0.088kW -1 Reactions that Maintain Redox w/o O2 glucose glycogen ATP ADP Anaerobic Glycolysis Efficiency of Anaerobic Metabolism G6P Pi ATP ADP F1',6' DP (P-6C-P) 2ATP 2ADP + 2P i 2(NADH + H+) Glycolysis 2NAD+ 2ATP 2ADP knp 2 (pyruvate) CH3--C -- COO|| O 2 (lactate) CH3--CH -- COO| OH glucose ----> 2 lactate - 196.7 KJ/mol from glucose: 2 ~P * 30.54 KJ = 61.08 kJ from glyc ogen: 3 ~P * 30.54 KJ = 9 1.63 kJ Efficiency = 61.1 / 196.7 * 100 = 31% Control of Metabolism [ATP] regulation is a problem given that demand can, especially in muscles, increase dramatically in a short period of time. The concept of pathway flux (overall rate -- mols/(product time) Equibrial and non-equilibrial reactions and control of flux PFK and glycogen phosphorylase as examples of nonequilibrial reactions. Inhibition and de-inhibition; activation. Association/Dissociation Constants as Organizers The concept of Kd What should be the relative values of Kd for AMP and ATP on the regulatory sites of PFK? Where should the Kd for AMP and ATP be compared to normal “resting” concentrations of these substances? Final Word on Metabolic Regulation Think about genetics, natural selection and the operation of negative feedback systems at the molecular level -- and their effects on the macrophenotype. Relationship Between Power Input and Output Power Input, P i Power Power Output, P o 0 Start Exercise Increase Level Time End Exercise Aerobic and Output Power in Organisms that Depend on Blood to Deliver Oxygen Possible Relationships Between Phosphagen and ATP During Heavy Exercise C~P Creatine Conc. ATP ADP Time Anaerobic and Phosphagen Metabolism: Unsustainable Exercise Relatiove Aerobic, Anaerobic & Phosphagen Metab During an Upwards P Transition ~P from ATP ~P from C~P ~P from Anaerobic Metabolism ~P from aerobic metabolism [lactic acid] knp Time Important Measures of Metabolic Performance • • • • MET (factorial metabolic scope) Absolute metabolic scope VO2 max Anaerobic Threshold Training and Anaerobic Performance The O2 Deficit - the Recovery O2 Concept EPOC at Higher Exercise Levels We may get to the next slides, but more likely on Monday Exceeding Maximum Aerobic Power EPOC At Aerobically Unsustainable Activity Levels Rapid and Slow Phases of Recovery Terms • Alactacid • Lactacid • Problems with these concepts? Maximum Sustainable Exercise Times and Contributions of Different Fueling Systems Metabolism -- ~P Homeostasis (reference) The Central Role of ATP in Cellular Energetics Storage Compounds (Carbohydrates, Fats) Catabolic Pathways (Breakdown of Complex Molecules, Aerobic and Anaerobic ~P production) (SUPPLY) (Spontaneous) Complex Molecules (poteins, lipids, complex carbs, protein complexes OR Movement and transport related processes requiring enery such as muscle contraction and active transport) ATP ADP + Pi Anabolic Pathways and Movement (DEMAND) (NonSpontaneous) knp Waste Products (Mainly CO2 and Water) Raw Materials (Amino Acids,Simple Carbs, etc; also protein conformations in the case of movement