* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
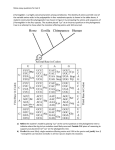
c-kit and the D816V Mutation The nucleus of the human cell contains 46 strings of DNA, called CHROMOSOMES, arranged in 23 pairs. Each chromosome actually consists of a number of smaller portions, rather like a string of beads. Each of these small units is called a GENE. There may be many thousands of GENES on each chromosome. • • • • • The DNA of the gene consists of a sequence of chemicals or nucleotides comprising either: Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) or Thymine (T) Adenine on one of the helix backbones of the DNA bonds or sticks to Thymine on the other, and Guanine bonds to Cytosine. These are called ‘base pairs’. Each gene is composed of between about 1000 and 1,000,000 base pairs. The genetic code as discovered by Watson and Crick in the 1950’s showed that a sequence of three nucleotides codes one amino acid. Thus, GAC codes the amino acid Aspartic acid (given code letter D), and GTC codes the amino acid Valine (given code letter V) . When the gene is activated the DNA sequence is translated via messenger RNA into a string of amino acids. Proteins like the Tyrosine Kinase enzymes are made of these amino acid strings. The c-kit gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 4 – called the q arm. This shows the normal c-kit DNA sequence for chromosome 4 at about the 816th. nucleotide from the beginning. Normal In this diagram the T (Thymine) at position 816 has been swapped for an A (Adenine) i.e. a mutation has taken place. This means that the triplet now reads GTC rather than GAC. GAC codes for Aspartic acid (D) and GTC codes for Valine (V) position 816 Normal Mutated Hence the correct notation for his mutation is D816V, showing that a point mutation at 816 resulted in a change of Amino acid from D to V. A different Amino acid is now present in the mutated enzyme – with dire consequences. Normal Mutated Val