* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
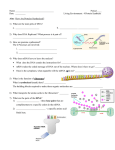
Lecture 6. GENE EXPRESSION Processing: pre-mRNA -> mRNA Myandina Galina Ivanovna professor, Ph.D.,Dr.Sc. In Eukaryotic nucleus Modification of pre-mRNA is taken place Eukaryotic genes have exons and introns Processing has 3 steps: • Capping - modification of 5’-end of mRNA • Polyadenilation - modification of 3’-end of mRNA • Splicing – removing of introns and joining of exons Both ends of Eukaryotic mRNAs are modified • At the 5' end, a cap is added consisting of a modified GTP (guanosine triphosphate). • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. Splicing of introns Lecture 7. Gene Translation: RNA -> Protein Myandina Galina Ivanovna professor, Ph.D.,Dr.Sc. The RNA Codons The aminoacyl-tRNA structure • Each tRNA specific for one amino acid and for a codon in mRNA • The amino acid is attached to the appropriate tRNA by an enzyme aminoacyltRNA synthetase specific for that amino acid as well as for the tRNA assigned to it. The anticodon binds the codon in the opposite direction • Anticodon (tRNA): 3'- CGA - 5' • Codon (mRNA): 5'- GCU - 3' The reading of codons in mRNA is 5' → to 3‘-end Prokaryotic ribosomes are of 70S Eukariotic ribosomes – 80S The 70S ribosome (prokaryotic) • The P site binds only to a peptidyl-tRNA molecule; that is, a tRNA with the growing peptide attached. • The A site binds only to the incoming aminoacyl-tRNA; that is the tRNA bringing the next amino acid.